SOP-42Q-MES0011 Part Number Maintenance
42Q Home > Shop Floor Control > Configuration > Part Maintenance

This edition applies to MES15 Portal 1.10 Application and all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new revisions.
Contents
- 1 SFDC Configuration Setup
- 2 Part Maintenance
- 2.1 Part Numbers List
- 2.1.1 Filter Results
- 2.1.2 Export List
- 2.1.3 Add Part Numbers
- 2.1.4 Standard Tab - Add Part Numbers
- 2.1.5 Flex Field Form
- 2.1.6 Flex Field Form - Add Field
- 2.1.7 Flex Field Form – Delete Field
- 2.1.8 Edit Part Number
- 2.1.9 Part Revision Maintenance.
- 2.1.10 Load BOM
- 2.1.11 Load Defect Opportunities
- 2.1.12 Delete Part Number
- 2.1.13 Print/Export Part Number
- 2.1.14 Copy Part Number
- 2.1.15 Obsolete Part Number
- 2.1.16 Import Part Numbers
- 2.1.17 Export Filtered Part Numbers (full)
- 2.1.18 Export Filtered Part Numbers
- 2.1 Part Numbers List
- 3 Appendix
- 4 Document Revision History
SFDC Configuration Setup
42Q’s powerful data collection system collects critical information from a plant’s shop floor, utilizing shop floor data collector, an intuitive tool developed by 42Q’s experienced manufacturing team. The aggregate information is stored in a cloud database, and available to MESWeb, where quality reports are generated. The 42Q system uses manual and automated barcode scanning to collect data for a product line or plant. Thus, 42Q plays an important role in maintaining unit histories and directing product movement on the manufacturing floor. The current version of 42Q includes configuration capabilities, which provide access to all sub-modules pages and their functionalities (view, add, edit, print/generate output files).
SFDC Configuration
To access SFDC Configuration, navigate to Shop Floor Control > Configuration > SFDC Configuration.
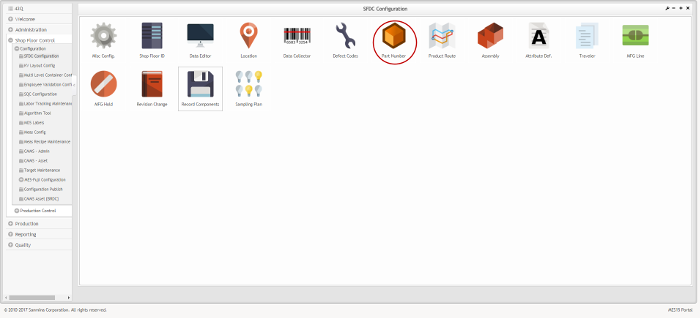
The main SFDC Configuration and sub modules page is displayed:
Figure 1: MES Portal – SFDC Configuration Sub-modules
NOTE: A user only has access to the modules assigned to his/her profile.
Part Maintenance
The Part Maintenance module defines part numbers and descriptions for products found in the SFDC System. A part number refers to the product ID of a top assembly, a base, or any component or sub-component making up a unit. A unit is an individual serial number assigned through SFDC. Scanning a serial number allows the system to track the unit from creation of a printed Traveler and/or serial number, through manufacturing, to shipping.
The Part Maintenance module provides the capability to Add, Delete, View, and Update Part Numbers.
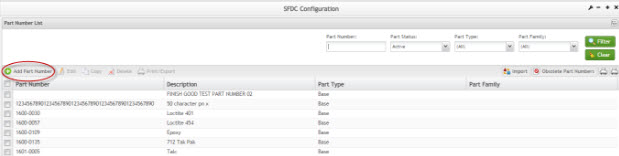
Part Numbers List
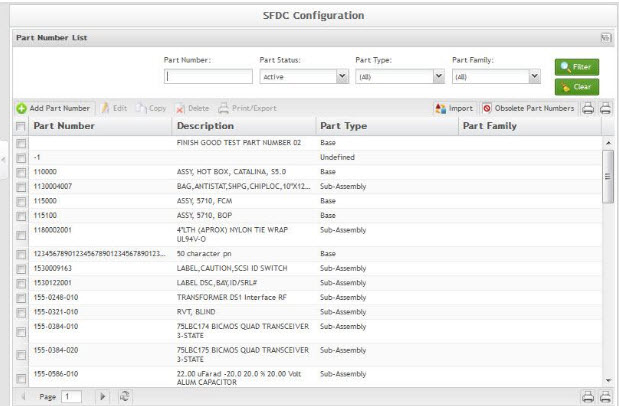
This functionality enables the user to list available part numbers in the database. The list results include the Part Number, Part Description, Part Type, and Part Family.
To access the part numbers list, select Part Maintenance from the SFDC Configuration Maintenance module.
The Part Number List window is displayed:
Figure 2: Part Number List
Filter Results
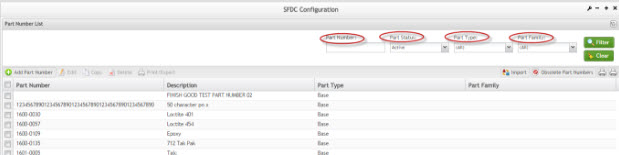
The user can filter the Part Number results by entering into the field Part Number, Part Status, Part Type, and/or Part Family.
Figure 3: Filter Results
1. Select Filter to view filter results
2. Select Clear to clear the fields and start a new search.
Export List
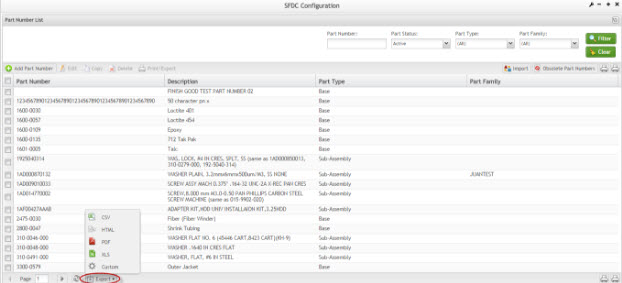
The user is able to execute the following actions: Add, Edit, Copy, Delete, Import, Obsolete Part Numbers, and Print/Export, Print/Export Filtered Part Numbers, Export Filtered Part Numbers and export the Part Number List as it is displayed in the page in several formats (.CSV, .HTML, .PDF, .XLS).
Figure 4: Export List
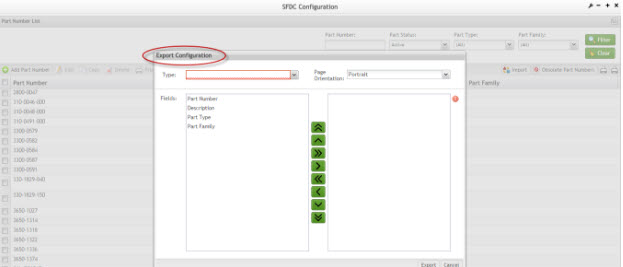
The user is able to custom the exported files by selecting Custom:
Figure 5: Export Configuration
1. Select the file type (.CSV, .HTML, .PDF, .XLS), the page orientation (portrait or landscape) and the fields to be displayed in the file to be exported by double clicking on the field or selecting the green arrows.
2. Select Export to save the file.
Add Part Numbers
This functionality enables the user to add part numbers to the database.
1. To add a Part Number, select Add Part Number from the Part Number List main page.
Figure 6: Add part number
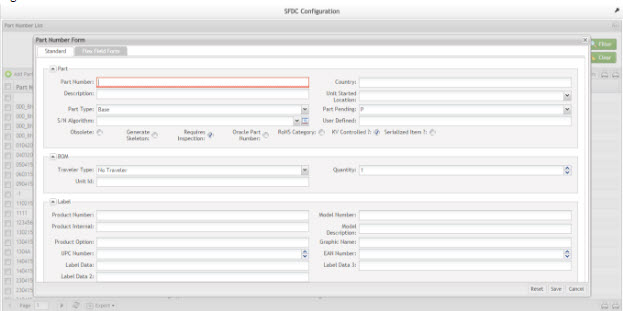
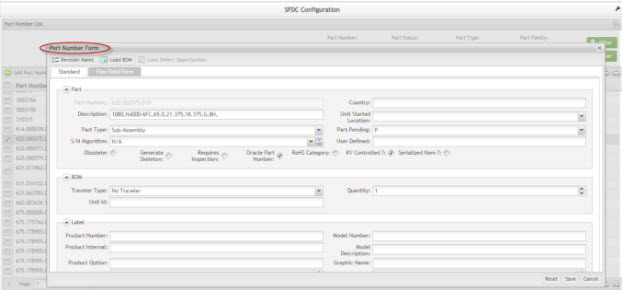
The Part Number Form is displayed:
Figure 7: Part Number Form
Standard Tab - Add Part Numbers
1. Populate the Part Number field. Other mandatory fields in red are auto-populated by default but may be modified as necessary.
2. Populate remaining fields as required.
Common Part Number field descriptions:
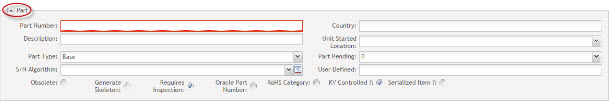
PART: This section defines the part number
Figure 8: Part Number Form
- Part Number: The unit part number. (50 Character limit)
As a general rule, the part number should match the Oracle part number.
- Description: The default description for the part number (150 Character limit).
As a general rule, the part description should match the Oracle part description.
- S/N Algorithm: Select the desired Serial Number Algorithm used during Release process. If the selected Algorithm is a Part Based Algorithm, the maintenance button is enabled for managing the appropriate fields.
- Part Type: Defines the part type
- Base: Base Part (top level assembly) This is the default when creating a part number
- Base/FIO: Base Part with Factory Installed Option
- FIO: Factory Installed Option
- FIO Kit: Factory Installed Option Kit
- ICP
- Internal Make Assembly
- Kit
- Make Buy Base/FIO
- Product Family: Defines a part number for use as a "Part Family" to associate other part numbers to. The user must first create a Part Family before adding parts to it.
- Spare
- Sub-Assembly: Sub-Assembly part that is merged to Base part type.
- Undefined
- Obsolete: Check-box to indicate obsolete part number.
- Generate Skeleton: Selecting it the part will use a mask to generate a serial number.
- Requires Inspection: By default it comes selected and it means thatthe part must be inspected.
- Oracle Part Number: Check if the part comes from Oracle.
- RoHS Category: It comes from Oracle. Ready only.
- KV Controlled: It comes checked by default and means that the part will be managed by Kit Verify.
- Serialized Item: if the Traceability Code (information from Oracle) starts with "S", this checkbox will be checked informing to Kit Verify that the part will have serial numbers.
BOM: This section defines Bill of Materials requirements of the part number.
Figure 9: BOM
- Traveler Type:
- Unit ID:
- Quantity: The quantity of units to appear on the traveler, as well as the quantity per unit serial number
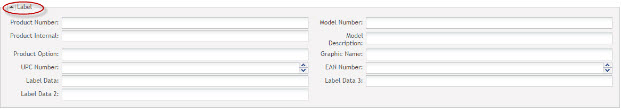
Label: This section defines additional part fields used for label printing.
Figure 10: LABEL Section
- All field data can be retrieved in label printing process.
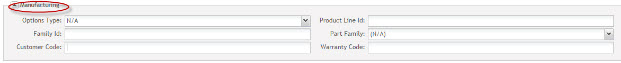
Manufacturing: This section defines manufacturing requirements of part number.
Figure 11: MANUFACTURING Section
- Part Family: Select the desired Part Family. Only parts defined as a "Product Family" Part Type are available for selection.
- Warrant Code:
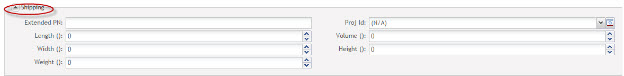
Shipping: This section defines dimensions of shipment requirements used in Containerization.
Figure 12: SHIPPING Section
- All field data used to define packing material dimensions, weight, skid and box quantities.
3. Click Save to create the Part Number, or click Cancel to cancel Part Number creation. To clear all filled fields, click on Reset.
4. The Part Number is created and available for tracking in the system.
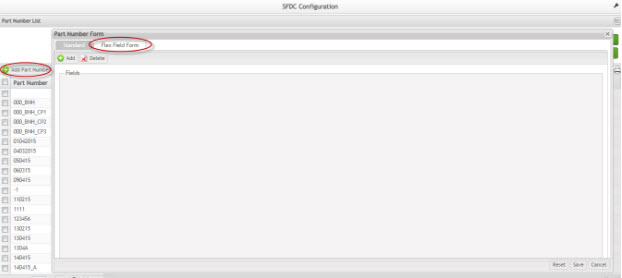
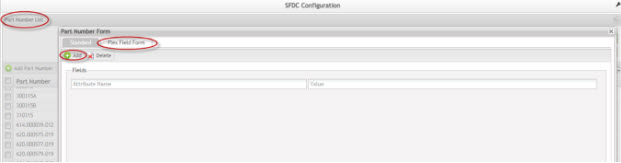
Flex Field Form
The Flex Form Field tab helps to create new fields in an existing form. When the user adds a new field in this form, the field will be reflected in all forms of the Part Number Maintenance.
Figure 13: Flex Field Form
It is possible to add or delete fields by selecting Add/Delete buttons.
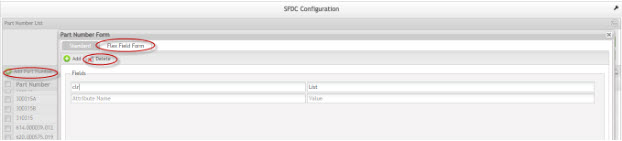
Flex Field Form - Add Field
Figure 14: Add Field
To add a new field, enter the attribute name and the respective value for it. The new attribute is considered a generic attribute but is not displayed at Generic Attribute module.
To edit the attribute, click over it. If the user edits the attribute name, it will be reflected in all parts that have this field. The value is not affected since the value is unique for each created field.
NOTE<u</u: If there is a generic attribute with the same name that the user is creating, an error message is displayed informing that it is not possible to create the attribute.
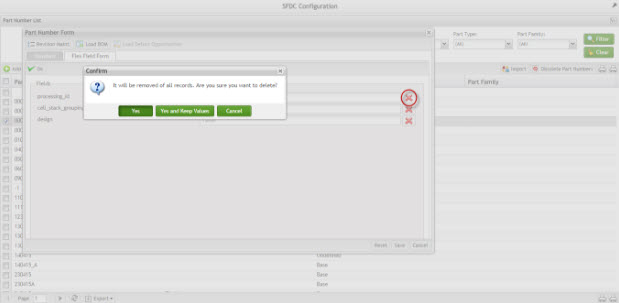
Flex Field Form – Delete Field
Figure 15: Delete Field
Figure 16: Delete Item From All Records
There are two options to delete the field:
1. The generic attribute will be removed from database: select Yes.
2. The generic attribute will be removed only from the page: select Yes and Keep Values.
Edit Part Number
This functionality enables the user to edit an existing Part Number. The Part Number field is unavailable for editing.
1. Select desired Part Number and select the Edit icon.
2. The Part Number Form is displayed:
Figure 17: Edit Part Number Form
3. Perform desired Part Number modifications. Reference section ''''2.1.2 Add Part Number for additional information on Part Number fields.
4. Select Save to confirm the update or Cancel to ignore updates.
5. The Part Number is updated.
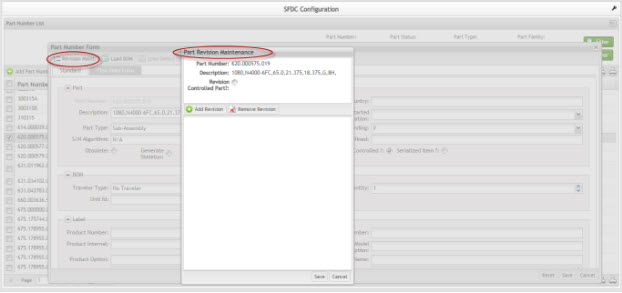
Part Revision Maintenance.
This functionality enables Revision Control for the selected Part Number. When releasing a Shop Order or performing revision changes, the revision is limited to the values contained in this section. Using revision control will lessen the risk of tracking units using an improper revision.
1. To Add/Delete a Part Number Revision, select Revision Maint from the Part Number form.
2. The Part Revision Maintenance window is displayed:
Figure 18: Part Revision Maintenance
3. Check the Revision Controlled Part to enable revision control. (Operators and users are only capable of releasing and/or changing unit revisions to those listed here).
4. Select Add Revision to add a revision to the selected Part. Enter desired Revision (double click) and select Update. To add another Revision, follow the same process.
5. Select Save to confirm, or Cancel to ignore.
6. To remove a revision from Part, select desired Revision and click the Remove Revision.
7. A confirmation is displayed. Select Ok to remove.
8. Select Save to confirm.
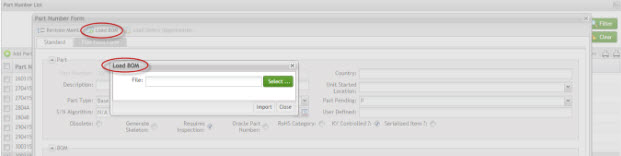
Load BOM
This functionality is part of DPMO (Defect per Million of Opportunities). It involves three modules: Defect Code, Generic attribute and Part Number Maintenance. Generic attribute module should be configured with the following options:
Generic attribute required:
- part_opportunities_reference_designator_column
- part_opportunities_process_column
- part_opportunities_joint_errors_column
- part_bom_revision_column
- part_bom_reference_designator_column
- part_bom_quantity_column
- part_bom_part_number_column
- part_bom_description_column
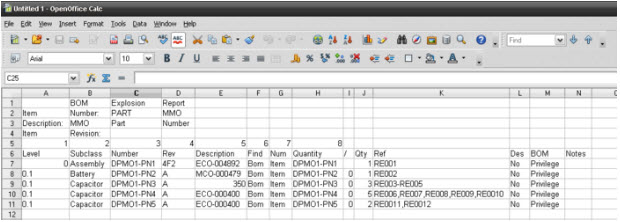
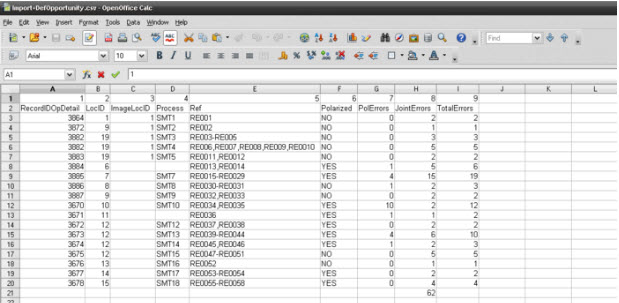
Sample of CSV file to be loaded:
Figure 19: Sample of BOM file
To load the BOM file, select the file and then select Ok.
Figure 20: Load BOM
A message telling all BOM was uploaded successfully is displayed and Load Defect Opportunities button becomes available.
The following information is displayed:
- BOM items information*:
- Part Number
- Quantity
- Revision
This information will be displayed for each record in the spreadsheet.
See the rules below to ensure that the calculations are correct.
To ensure that the calculations are correct, the following rules must be validated:
- 1º rule:
- This rule checks the total of opportunities. After all the calculations, this rule is displayed.
- There will be 1 record for the Total number of opportunities, for a part number, which will have "Total" as the process name.
- The total number of component opportunities will be the count of the components (the sum of the quantity field in the BOM that was imported).
- The total number of placement opportunities will be the count of the components (the sum of the quantity field in the BOM that was imported).
- The total number of termination opportunities will be the sum of the termination counts (Column H, "JointErrors", in the above sample. The total number of assembly opportunities is 1.
- 2º rule:
- This rule is executed to check if there is a mechanical process or not. Mechanical processes are considered when missing process information, process filled as Mechanical, No Ref. Designator or quantity information than Qty. Ref Designator.
- Create a record to hold the data with the part key and process name populated.
- The number of component opportunities will be the count of reference designators that are added at that process.
- The number of placement opportunities will be the count of reference designators that are added at that process.
- The number of termination opportunities will be the sum of the termination opportunities for the reference designators at that process. The number of assembly opportunities is 0.
- 3º rule:
- This is to check if the mechanical calculation is correct. The number of component opportunities will be the number of total component opportunities minus the sum of the component opportunities in the other process records.
- The number of placement opportunities will be the total placement opportunities minus the sum of the placement opportunities in the other process records.
- The number of termination opportunities will be the number of total component opportunities minus the sum of the component opportunities in the other process records. The number of assembly opportunities will be 1.
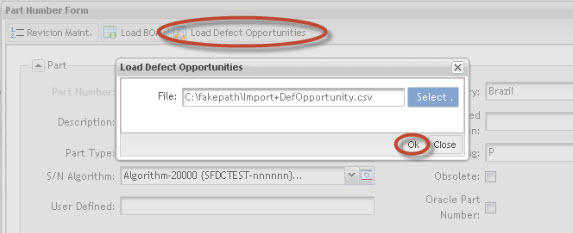
Load Defect Opportunities
This functionality is part of DPMO (Defect per Million of Opportunities). The Load Defect Opportunities button will be available after import a BOM file.
Generic attribute should be configured to the following options:
- part_opportunities_reference_designator_column
- part_opportunities_process_column
- part_opportunities_joint_errors_column
- part_bom_revision_column
- part_bom_reference_designator_column
- part_bom_quantity_column
- part_bom_part_number_column
- part_bom_description_column
Figure 21: Load Defect Opportunities
Sample of CSV file to be loaded:
Figure 22: Sample of CSV file
The file is loaded and a success message is displayed informing all Defect Opportunities were loaded.
The following information is displayed:
BOM items information*:
Part Number
Quantity
Revision
Defect Opportunities information*:
Process Name
Ref Des
Terminal
- These information will be displayed for each record filled in the spreadsheet.
Delete Part Number
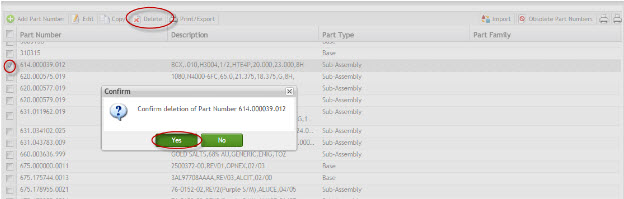
This functionality enables the user to delete an existing part number.
NOTE: It is not possible to delete an existing Part Number if activity records have been recorded for it.
1. Select the Part Number record to be deleted and select Delete. A confirmation message is displayed.
Figure 23: Delete Part Number
2. Select Yes to confirm or No to cancel deletion operation.
3. The Part Number is deleted from the database, provided no activity records had been recorded for it.
Print/Export Part Number
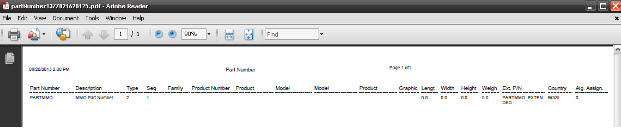
This functionality enables the user to print/export an existing part number. The report results include the Part Number, Description, Part Type, Print Sequence, Part Family, Product Number, Product Internal, Model Number, Model Description, Product Option, Graphic, Length, Width, Height, Weight, and the External Part Number.
1. Select the desired Part Number and click the Print/Export button. A report is generated and the user is able to save the file or print it:
Figure 24: Part Report
Copy Part Number
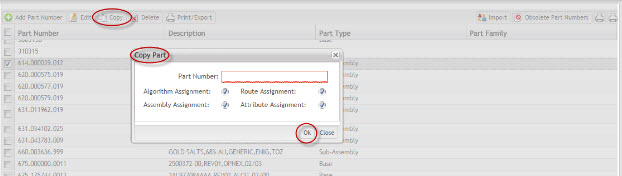
This functionality enables the user to copy existing Part Number information to a new Part Number.
1. To copy an existing Part Number, select the desired Part Number; then select Copy. The Copy Part page is displayed:
Figure 25: Copy Part dialog
2. Enter the new part number.
3. Select the desired check boxes to choose other assignments to copy to the new part number.
- Algorithm Assignment
- Assembly Assignment
- Route Assignment
- Attribute Assignment
4. Select Ok to confirm, or Close to cancel copy.
5. The new Part Number is created and added to the part table.
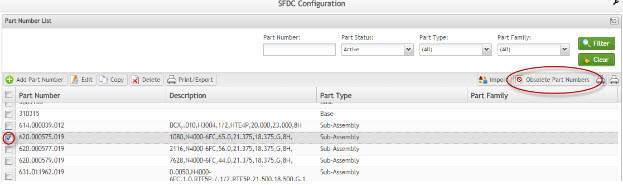
Obsolete Part Number
This functionality enables the user to set a Part Number as obsolete.
NOTE: There are situations that the part number cannot be set to obsolete:
- It is not possible to set a Part Number as obsolete when assigned to a pending Shop Order (SO status different other than "R"). If an attempt is made, an error message is displayed: "The Part Number cannot be set as "Obsolete". There is at least one pending Shop Order assigned to it."
- It is not possible to set a Part Number as obsolete when assigned to a test configuration. If an attempt is made, an error message is displayed: "The Part Number cannot be set as "Obsolete". There is at least one Test Configuration using it on Kit Verify."
1. To flag a Part Number as obsolete, select the desired part number from the Active list and then select Obsolete Part Numbers.
Figure 26: Obsolete Part Numbers
2. The Part Number is set as obsolete.
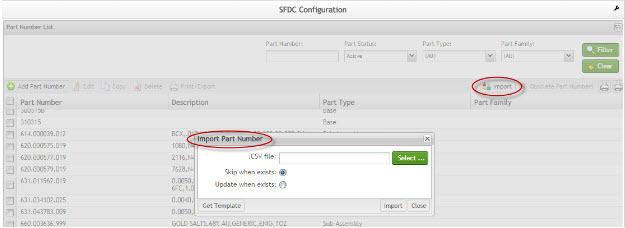
Import Part Numbers
This functionality allows the user to import some parts at the same time.
1. Select Import to choose the file to be imported.
Figure 27: Import Part Numbers
2. Select Get Template to acquire the CSV file. Enter the data and save it locally. Select the saved file and then select Ok. A Success message is displayed.
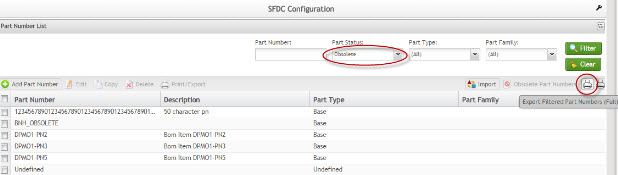
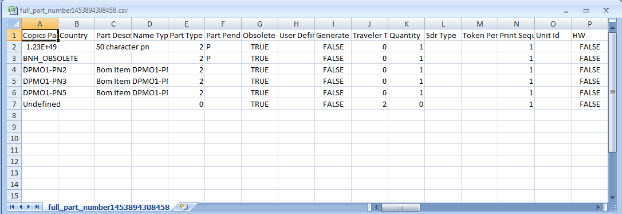
Export Filtered Part Numbers (full)
This functionality generates a CSV output file for all Part Number fields. No report is generated for this option.
1. To print/export filtered part numbers (Full), perform the filter and select Print/Export Filtered Part Numbers.
Figure 28: Export Filtered Part Numbers (Full)
A report is generated and the user is able to save the file or print it.
Figure 29: Export Filtered Part Numbers (Full) results
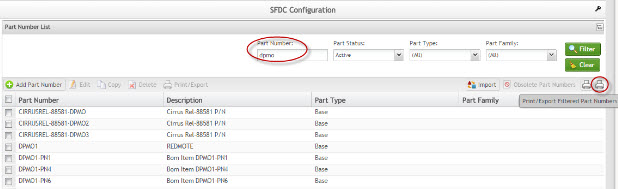
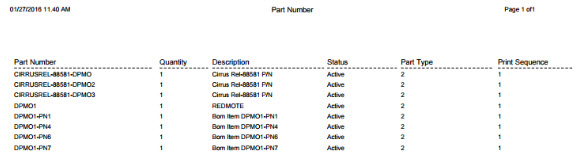
Export Filtered Part Numbers
This functionality generates an output file with the current filtered part numbers. The report results include the Part Number, Quantity, Description, Status, Part Type, and Print Sequence.
1. To export filtered part numbers, select Export Filtered Part Numbers.
Figure 30: Export Part Numbers
2. A report is generated and the user is able to save the file or print it.
Figure 31: Export Filtered Part Numbers
Appendix
Glossary
Access Control
A module that will set the permissions for users and external customers of 42Q
Administrator
The System Administrator has full access - all plants, all reports, all users.
Component
A component is a specific piece of data that appears on a label, for example: bar code, part numbers, graphic images, line or text. Hence, label components are broken down into several different types: text, graphic images, MES database values, or a combination of text and database values.
Framework
In software development, a framework is a defined support structure in which another software project can be organized and developed. A framework may include support programs, code libraries, a scripting language, or other software to help develop and glue together the different components of a software project.
SFDC Configuration
The rules used to define how SFDC collects data, provides analysis, controls processing and maintains unit histories.
Site Minder
Universal login of 42Q
Username
The username is the siteminder username (or a partial string).
Document Revision History
| Date | Author | Title | Version | Change Reference | Approved by |
| 20/08/2013 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | This is the first revision of MES Part Maint User's Guide | |
| 10/02/2014 | Ashley Martin | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | Grammar and images review | |
| 12/02/2014 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | Formatting | |
| 08/12/2015 | Kala Burson | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | Document formatting. | |
| 26/01/2016 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | v 1.10 | Added new Functionalities:
| |
| 04/03/2016 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | v 1.10 | Updated Oracle Occurrences to ERP | |
| 10/07/16 | Benjamin Cavanaugh | Technical Writer | v 1.10 | Converted for 42Q | |
| 8/02/17 | Lucas Hopkings | Technical Writer | v 1.10 | Edited images for 42Q. | |
| 04/03/17 | Martha Jordan | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | Rewrite SFDC intorductory paragraph according to current 42Q functionality | Bob Moss |