42Q-MES0136-C OEE Configuration
42Q Home > Reporting > OEE Reports > OEE Configuraton
This edition applies to MES 15 Portal 1.0 and all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new revisions.
Contents
OEE Configuration
The OEE Configuration modules allow users to define the following:
- Shift
- Plant Calendar
- Work Center
- Root Cause Category
- Root Cause
- Repair Code Category
- Repair Code
Users complete the following tasks within OEE:
- Map Tag IDs to Assets (Tag Mapping)
- Define Up/Down Thresholds for Asset Types
- Import Tag Mapping
- Import Up/Down Thresholds
- Set Target UPH for Mfg Line, Process Part Number, and Shop Order
Prerequisites
The OEE application utilizes data configured in CMMS Asset (Shop Floor Control > Configuration > CMMS Asset). The following CMMS categories must be predefined. Associations are noted throughout this document.
- Asset
- Asset Type
- Problem Type
- Problem Category
- Problem
- Location
Shift
The Shift submodule is utilized by supervisory personnel to define time and days of operation to the various shifts operating in their plants in order to accurately measure OEE availability. Administrators assign Shift Names and Shift Codes to scheduled shifts, and edit and add shifts as needed.
1. Navigate to Shop Floor Control > Configuration > OEE > Shift. The Shift’s main page displays.
Figure 1: Shift Main Page
2. Users may add, edit, and enable/disable the shift, and search for shifts using the following filters:
- Shift Name
- Shift Code
Add Shift
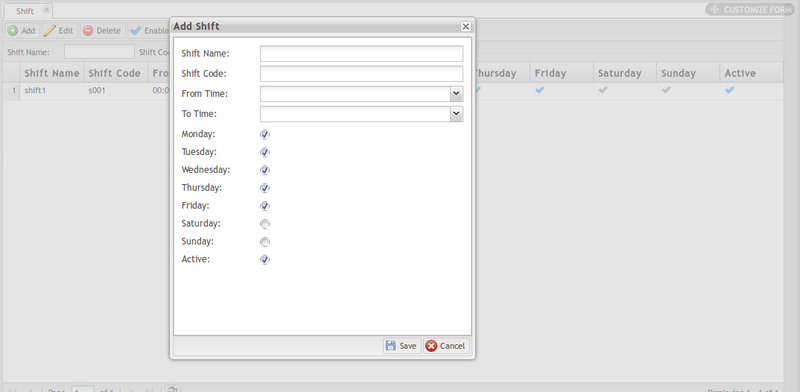
1. Select the Add button on the top menu bar to create a new shift entry.
Figure 2: Add Shift
2. The following fields are available:
- Shift Name: Provide a name to differentiate the Shift.
- Shift Code: Provide a Code for the Shift.
- From Time: Note the Shift’s start time with the drop-down calendar provided.
- To Time: Note the Shift’s end time with the drop-down calendar provided.
- Workdays: Select all days that have shifts assigned. Available days are Monday - Sunday. NOTE: Monday-Friday are selected by default.
- Active Status: Mark active shift days by activating the checkmark. Shifts marked as active are enabled in the system. The default selection is Active.
Edit Shift
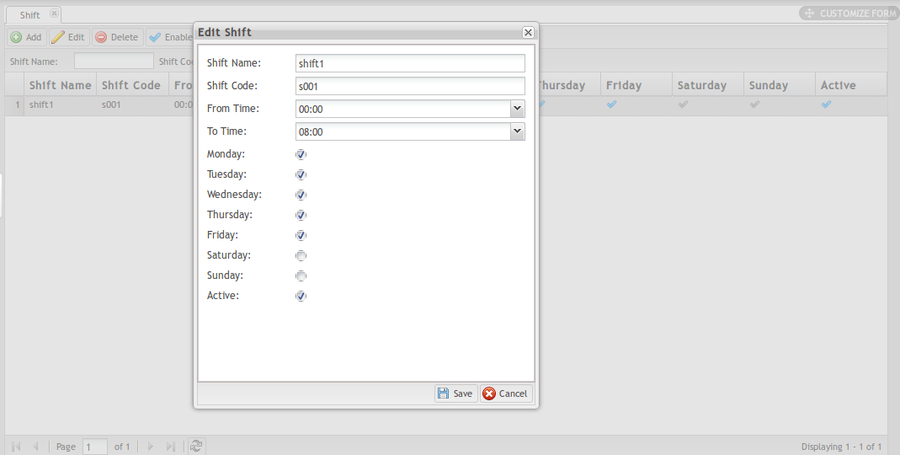
1. Select one Shift from the list then click Edit to open the Edit Shift page.
Figure 3: Edit Shift
2. Change the Shift Name, Shift Code, From Time, To Time as needed.
3. Change the workdays: A Checkbox signifies there is a working shift assigned to the day. Change the Active status as needed. When the checkbox is selected the shift is in active status.
4. Click Save to save the changes of shift or Cancel to leave the Edit Shift page.
Enable/Disable Shift
1. Select the desired shift by double clicking on the line of data.
2. Select Enable/Disable to change the shift status from active/inactive into inactive/active.
Plant Calendar
The Plant Calendar is a planning tool that allows administrators to add or remove special shifts from the work schedule (such as holidays, or extra work days, e.g. Sundays), without affecting the regular work shift calendar. NOTE: Plant Calendar is not a standard monthly view calendar.
1. Navigate to Shop Floor Control > Configuration > OEE > Plant Calendar to access the plant calendar main page.
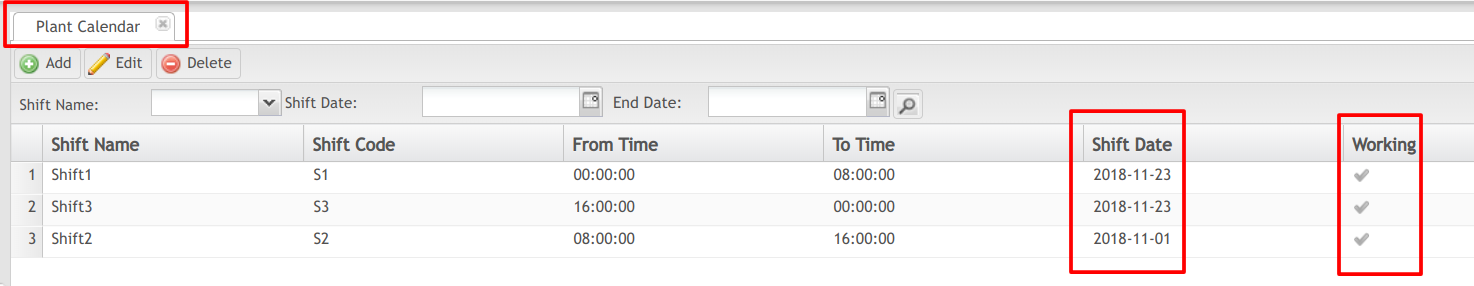
Figure 4: Plant Calendar Main Page
- The Plant Calendar screenshot above shows all 3 Shifts that run at this plant; they are scheduled as not working on the Friday following Thanksgiving holiday. The information will be automatically recorded as downtime by the MES.
- Users can Add, Edit, Delete, and Search the Plant Calendar by Shift Name or Shift Date.
Add Plant Calendar
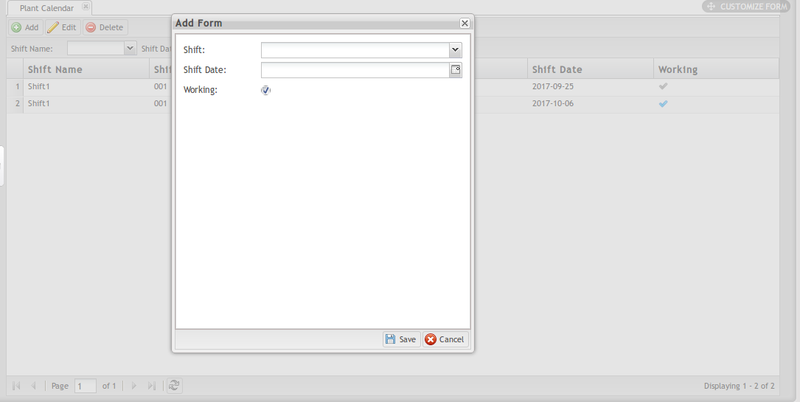
1. Select the Add button to open the Add form.
Figure 5: Add Plant Calendar
- Select the Shift and Shift Date using the drop-down menus provided.
- Select Working if the shift is scheduled to work on the given date; deselect if the shift is off duty on the selected date.
- Select Save to save the new plant calendar, or cancel to exit the add form.
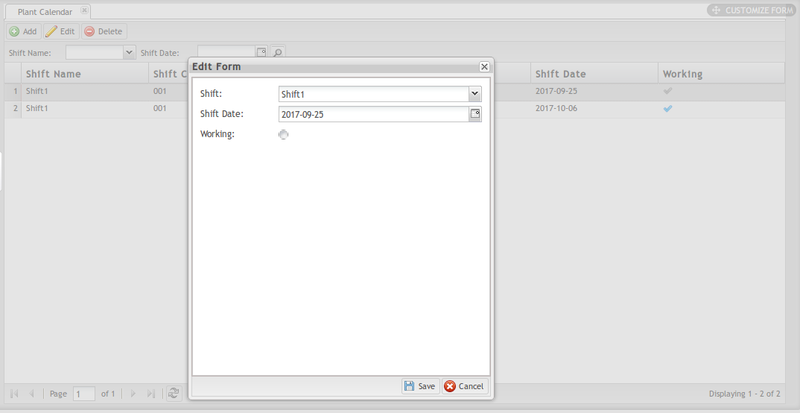
Edit Plant Calendar
1. Select the Plant Calendar for modification then select the Edit icon to open the Edit Form.
Figure 6: Edit Plant Calendar
2. Change the Shift and Shift Date.
3. Select Working if the shift is scheduled to work on the selected date; deselect if the shift is off duty.
4. Click Save to save the changes in the plant calendar, or cancel to exit the edit form.
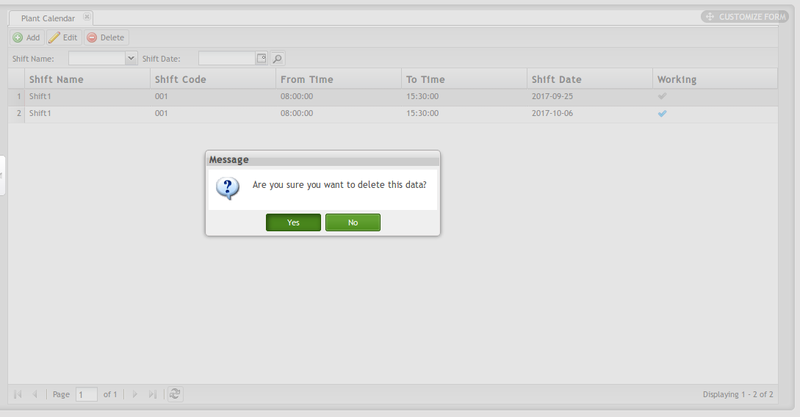
Delete Plant Calendar
1. Select the Plant Calendar, then click Delete button.
Figure 9: Delete Plant Calendar
2. A message window displays asking the user to confirm the action. Select Yes to delete the Plant Calendar, or No to cancel.
Work Center
The Work Center defines a group of machines that build the same product on a production line or shop floor. Work Center is a configuration tool used by managers to:
- Designate the Work Center Name
- Assign an Asset to the Work Center.
Assigning the asset is a critical step that allows data to move between portals within the MES system, thus providing superior traceability and data collection. NOTE: Assets are configured within the CMMS Asset portal (Shop Floor Control > Configuration > CMMS Asset).
1. Navigate to Shop Floor Control > Configuration > OEE > Work Center to access the Work Center’s main page.
Figure 8: Work Center Main Page
2. Users can Add, Edit, Delete, and search the Work Center.
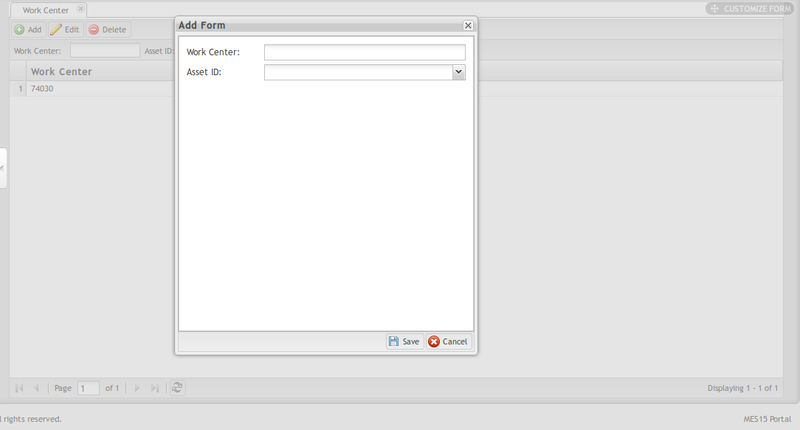
Add Work Center
1. Select the Add Button to open the add form.
2. Enter the Work Center name
3. Select the Asset ID for the machine running on the work center.
4. Select the Save button to add the new Work Center or Cancel to exit the field.
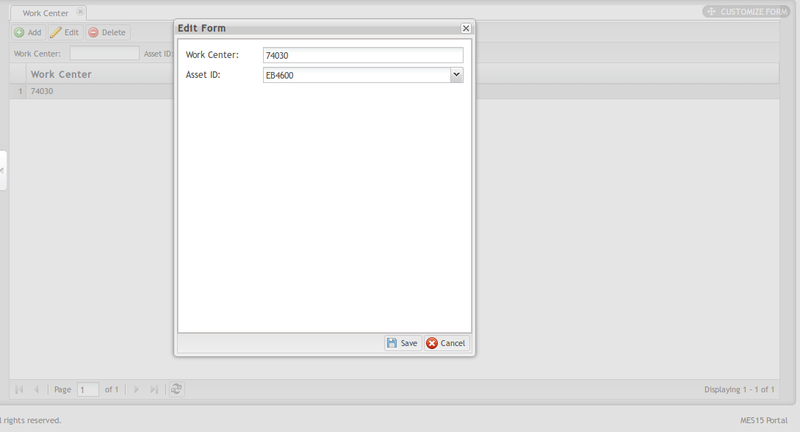
Edit Work Center
Select one Work Center from the list then click Edit to open the Edit form.
Figure 10: Edit Work Center
2. Change Work Center or Asset ID as needed.
3. Select Save to save the updates, or Cancel to close the edit form without saving.
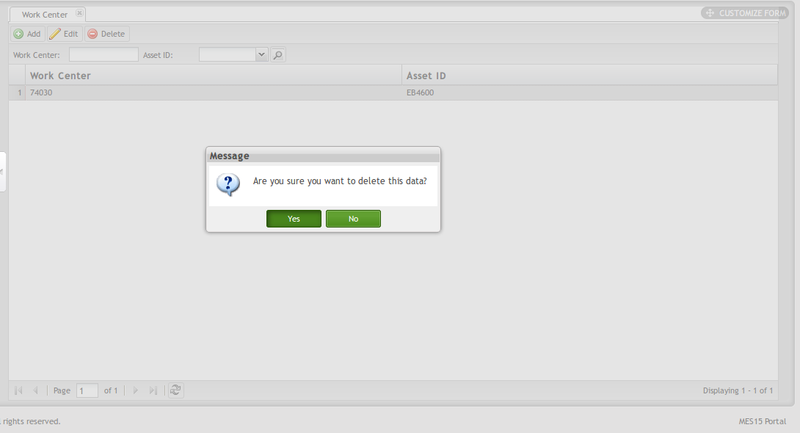
Delete Work Center
1. Select the Work Center, then click Delete.
Figure 11: Delete Work Center
2. A Message window displays asking the user to confirm the action.
3. Click Yes to delete the Work Center, or click No to cancel.
Root Cause Category
Root Cause Categories are broad descriptions of machine downtime problems. Possible manufacturing Root Cause Category examples include: Process, Energy, System, and Maintenance. Engineers may also add new root causes or edit associated root causes from the Category submodule.
Root Cause Categories are organized in a parent/child hierarchy in a visual tree format. Main categories are represented by yellow folders (parents); blue file folders represent subcategories (children).
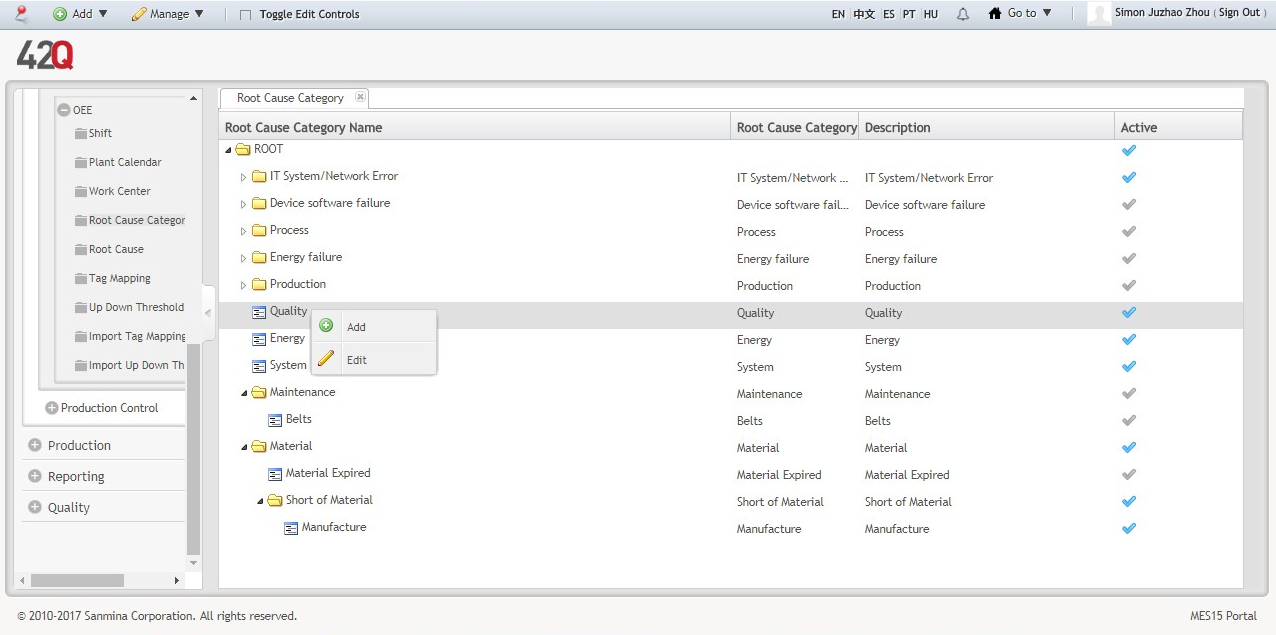
1. Navigate: Shop Floor Control > Configuration > OEE > Root Cause Category.
2. To add/edit a category, select the category’s location within the hierarchy by right clicking on the parent or child icon. A pop-up window displays, which allows the user to Add a new category or Edit the selected category. (See figure, below.)
Figure 12: Add Child Root Cause Category
Add Root Cause Category
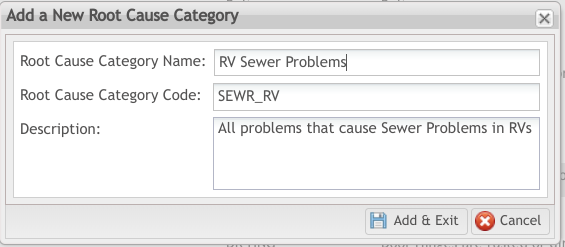
1. A new window displays, with the following fields available for entry (see figure, below):
- Root Cause Category Name (Mandatory)
- Root Cause Category Code (Mandatory)
- Description (Optional)
2. Select the Add & Exit icon to save the new root cause category as a “child” to the selected “parent” Root Cause.
![]() TIP: Users can add corresponding Root Causes directly to Root Cause Category in Edit mode.
TIP: Users can add corresponding Root Causes directly to Root Cause Category in Edit mode.
3. GENERAL NOTES about Categories:
- Parent folders are denoted by a yellow folder icon.
- Child folders are denoted by a blue folder icon.
- Users may not add more than 5 levels to one root cause category.
- Only active Parent categories (denoted by a blue checkmark in the Active column) are available for edit. Likewise, children categories cannot be added to inactive parent categories.
- Children categories display indented beneath their parent.
- If a second child category is added to the first child, its position moves to the left side of the screen to signify parent hierarchy (and changes to yellow file folder icon)
Figure 13: Add a New Root Cause Category Pop-up Window
Edit Root Cause Category
To edit a Root Cause Category:
1. Right click on the root cause to activate the Edit Root Cause Category window.
2. Modify any of the fields:
- Root Cause Category: Select a different category from the drop-down list.
- Root Cause Category Name: Change the Name of the Root Cause Category
- Root Cause Category Code: Change the Code for the Root Cause Category
- Description: Add or change the description.
- Active: Change the status of the root cause category by activating or deactivating the checkmark. Active = Checked.
Edit Root Cause
Root Causes associated with the selected category may also be added/edited directly from the Edit Root Cause Category submodule by selecting the Root Cause Tab.
Figure 14: Edit Root Cause Category: Root Cause Tab
To Add a new Root Cause, select Add.
1. Complete the fields in the new window: Root Cause Code, Root Cause Name, Description, Active/Inactive status.
2. Select Add & Exit or Close to cancel.
To Edit a Root Cause:
1. Select the Root Cause in the list by activating the checkmark next to its data.
2. Modify any of the fields in the new window: Root Cause Code, Root Cause Name, Description, Active/Inactive status.
To change the statusof a Root Cause:
1. Select the Root Cause by activating the checkmark.
2. Select Enable/Disable.
Root Cause
Users may add and edit root causes directly from the Root Cause Category submodule, or within the Root Cause submodule of OEE. It is important that a direct relationship between Root Causes and Root Categories exist.
https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/0r_ik4hZgQRRk0Rq2JUtyWsyGV1jTkU-Nv_Yt3gamWHpJYnrTh9B7ke7AX717y12QXbST0Dg4iSNiMylVzqM_iD8GgjqlEkHLTS8d3e4iPBf2xVVdsHr-TYqm249EI6pMdRnvsfYTIP: Chart Root Cause Categories and Root Causes in a table or spreadsheet first. See this example.
Examples of root causes pertaining to a manufacturing environment include: Material Issues, Shortage of Operators, Unscheduled Maintenance, Change Over, End of Shift Cleaning, and Tool Change.
NOTE: Selecting exact root causes assists engineering teams in troubleshooting machine downtimes, thereby creating strong OEE data to achieve optimal asset productivity.
Add a Root Cause
To create a new Root Cause:
- 1.Go to: Shop Floor Control > Configuration > OEE > Root Cause.
- Select theAdd button.
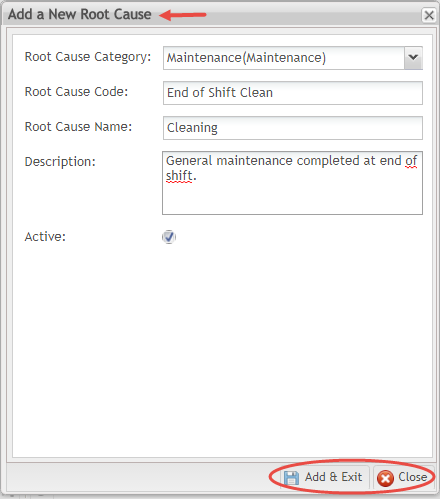
- The Add a New Root Cause window displays with the following options:
- Root Cause Category (Mandatory) Select the appropriate category from the drop-down menu. Categories are listed as icons in a tree format according to parent/child relationship.
- Root Cause Code (Mandatory) Enter the Root Cause Code into the text field.
- Root Cause Name (Mandatory) Enter the Name of the Root Cause in the text field.
- Description (Optional) Add any additional instructions that may be necessary.
- Active (Checkmark) Select the checkmark to activate the Root Cause.
Figure 15: Add New Root Cause
Edit Root Cause
To edit a Root Cause:
- Select the Root Cause from the Root Cause list.
- Modify any of the fields:
- Root Cause Category: Select a different category from the drop-down list.
- Root Cause Code: Change the Code for the Root Cause selected.
- Root Cause Name: Change the Name of the Root Cause selected.
- Description: Add or change the description.
- Active: Change the status of the root cause by activating or deactivating the checkmark. Active = Checked.
Export Root Cause
Users may also Export Root Cause information for quick access from a local pc or laptop.
- Select the Root Cause to Export.
- Select the Export icon.
- The data automatically downloads in .csv file onto the user’s local drive and is available to save, print, or share as desired.
Root Cause Category & Root Cause Relationship Example
The screenshot below shows a Root Cause Category and corresponding Root Causes surrounding uneven doors on a Recreational Vehicle (RV) Rental Lot.
![]() TIP:Read more about the relationship between problems, root causes, and repairs in this RV Rental Problem/Root Cause/Repair Example.
TIP:Read more about the relationship between problems, root causes, and repairs in this RV Rental Problem/Root Cause/Repair Example.
Tag Mapping
The Tag Mapping feature links (tags) assets to program logic control (PLC) hardware tools, used in conjunction with open platform communication (OPC) servers.
Asset is Down → PLC Hardware receives signal → OPC converts data → 42Q MES receives downtime data → OEE calculates reports.
Users create a Tag ID for each asset linked to programming logic control (PLC) tools. Data from the PLC is then fed to an OPC server that sends the converted data to 42Q’s MES. The mapping process allows manufacturers with multiple machines and production floors to quickly identify and locate the source of the downtime event.
Users may search, add, edit, or enable/disable a Tag ID via the Tag Mapping submodule.
Figure 6: Tag Asset Mapping Main Screen
Search/Filter Tag ID
1. Users may search according to the following criteria, located on the top menu bar of the Tag Asset Mapping submodule:
- Tag ID
- Asset ID: Drop-down menu provided
- Status;;;: Drop-down calendar allows the user to choose: Disabled, Enabled.
2. Select filtering option(s).
3. Choose the search icon (e.g. magnifying glass).
Add Tag ID
1. Select Add from the top menu bar.
2. Complete the fields in the pop-up window:
- Tag ID: Enter the ID associated with the asset in the PLC system.
- Asset ID: Select the Asset ID from the drop-down menu. (NOTE: Asset IDs are configured in CMMS Asset (Shop Floor Control > Configuration > CMMS Asset).
- Status: Mark the Tag ID as active (checked) or inactive (unchecked). Default is active (checked).
3. Select Save to add the new Tag ID or Cancel to exit the field.
Figure 7: Add Tag Asset Mapping
Edit Tag ID
To modify a Tag ID:
1. Select the Tag ID by highlighting the line of data.
2. Select Edit from the top menu bar.
3. Change any of the fields using the pop-up window.
4. Select Save to save changes or cancel to exit the field.
Figure 8: Edit Tag Asset ID
Figure 9: Edit Tag Asset Mapping
Enable/Disable Tag ID
To change the status of a Tag ID:
1. Select the Tag ID by highlighting the line of data.
2. Select Enable/Disable from the top menu bar.
3. NOTE: Selecting Disable moves the Tag ID to the bottom of the list. If the list is extensive, enter the Tag ID in the search field, then select Enable.
Glossary of Terms
- Availability: Machine Downtime, according to duration. Takes into account all machine downtime to include minor stoppages, slow production, and idling. Calculated as: Operation Time/Planned Production Time = Availability.
- KPI: Key Performance Indicators
- Loading: Represents the percentage of time that an operation is scheduled to operate compared to the total Calendar Time that is available. Calculated as: Scheduled Time/Calendar Time = Loading
- OEE: Overall Equipment Effectiveness is a manufacturing metric that identifies the percentage of productive manufacturing time according to Quality, Performance, and Availability. It is the single best metric for identifying losses, benchmarking progress, and improving the productivity of manufacturing equipment. Calculated as: Availability x Performance x Quality = OEE
- Performance: A measure of productivity, specifically the speed at which parts are built. Calculated as: Actual Rate/Standard Rate = Performance
- PLC: Programming Logic Control
- OPC Server: Open Platform Communication Servers
- Quality: The percentage of parts that meet quality standards without rework. Calculated as: Good Units/Total Units = Quality
- TEEP: Total Effective Equipment Performance. Calculated as: Loading x OEE.
Document Revision History
| Date | Author | Title | Version | Change Reference | Approved by |
| 09/06/17 | Helena Wang | Technical Writer | A1 | This is the first edition of the OEE Work Instruction Phase II | |
| 10/13/17 | Martha Jordan | Technical Writer | A2 | English grammar/New features | |
| 11/14/17 | Martha Jordan | Technical Writer | A3 | Add Phase III | Simon Zhou |
| 11/17/17 | Martha Jordan | Technical Writer | A4 | Screenshot updates | Simon Zhou |
| 11/09/17 | Martha Jordan | Technical Writer | A5 | Move to Separate document page and combine modules: OEE configuration. Add changes per 11/2018 OEE upgrade. | Simon Zhou |