SOP-42Q-MES0004 Data Collector Maintenance
This edition applies to MDS Portal xx-x Application and all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new revisions.'
Introduction
The Shop Floor Data Collection System (SFDC) communicates interactively with the Customer Order Processing System (COPS), and Statistical Process Control/Statistical Quality Control (SPC/SQC). The Manufacturing Data System (MDS) makes the communication between these systems possible.
SFDC provides real-time information used by SPC/SQC and MESWeb to create quality control reports. The data configuration for SFDC PC is handled within the Manufacturing Data System (MDS), which is a complete factory automation system. The SFDC System uses barcode scanning, both manual and automated, to monitor and control a single product line or an entire plant. SFDC Configuration collects data, provides analysis, maintains unit histories, and controls product movement on the manufacturing floor.
The system provides Access Control between the modules of the application, including the functionalities of each page. The current version has an SFDC Configuration page which provides access to all screens and its functionalities (view, add, edit, delete, print and generate output file), and a View-Only mode screen which only supports view, print and output to file; to support these screen modes, the MDS user or group of users have specific profiles, which provides specific access to MDS screens and functionalities.
Data Collector Maintenance
Data Collector Maintenance provides definitions in the SFDC database to associate a Device Number to a Data Collection Location name.
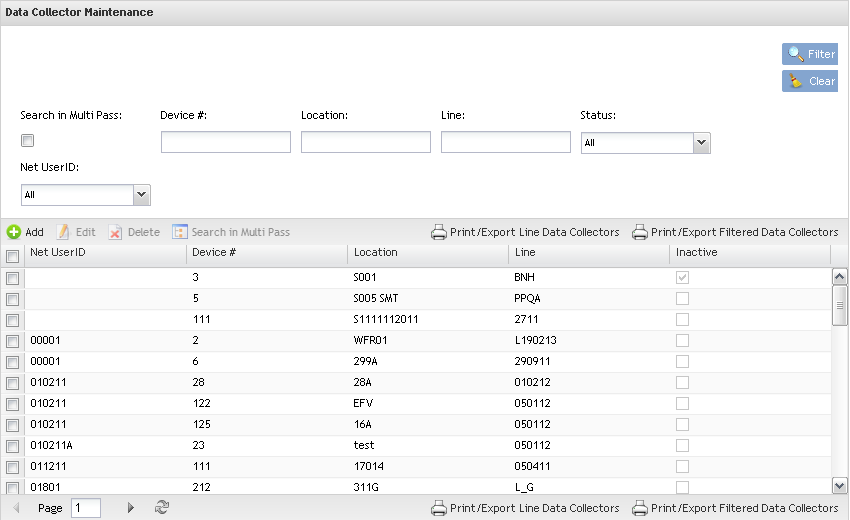
- To access the Data Collector module, click on Data Collector from the SFDC Configuration Maintenance menu. The main Data Collector List screen is displayed.
Figure 1: Data Collector List
In accordance with the associated Location status, the line in the Data Collector list is displayed in the colors below:
(THIS IS A FEATURE TO BE DEVELOPED)
- Status = 20 with process name: green
- Status = 20 without process name: orange
- Status = 28 with process name: dark green
- Status = 28 without process name: dark orange
- Status = 25: red
- Status = 29: dark red
- Status = 30: blue
- Other Status: black
Note: The colors are based from configuration in the Location Maintenance module.
Data Collector definitions in the SFDC database to associate a Device Number to a Data Collection Location name.
Device Number refers to an actual Data Collector number. Data Collector Device Numbers range from 1-999.
- CS9400 Data Collectors and PCC port addressing is limited to a range from 1-320 (each PCC has 5 communication ports with up to 32 Devices per port totaling 320 devices).
- NetDC Device Numbers are limited to a range from 321-999.
- Emulators can access any Device Number from 1-999.
CS9400 Data Collectors and PCC port addressing Device Numbers are outlined as follows:
| PCC Brd 1 Port 1 | Device numbers 001-032
|
PCC Brd 1 Port 2 | Device numbers 033-064
|
PCC Brd 1 Port 3 | Device numbers 065-096
|
PCC Brd 1 Port 4 | Device numbers 097-128
|
PCC Brd 1 Port 5 | Device numbers 129-160
List Data CollectorsBased on the actual SFDC Configuration, a list is displayed with all Data Collectors.
Filter Data CollectorsThis functionality enables user to perform searches. There are four available filter fields:
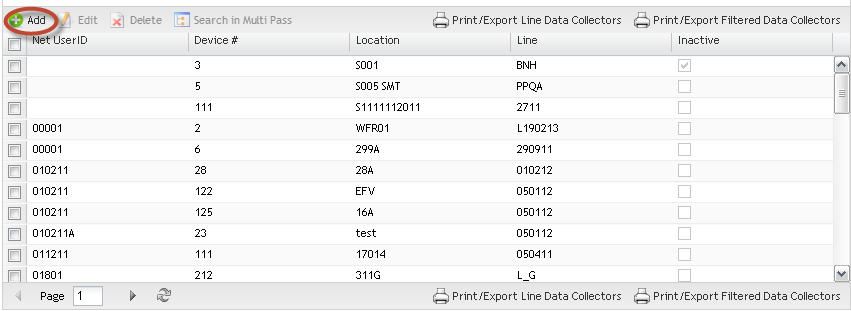
Add Data CollectorsThis functionality enables the user to add Data Collectors to the database.
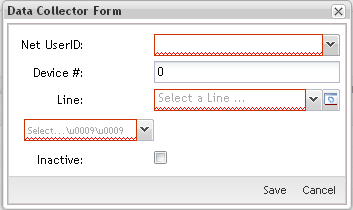
Figure 3: Add Data Collectors – Data Collector Form
Note: Line and Location fields have a Manage button that enables the user to manage these fields during Data Collector creation.
CAPTURAR IMAGEM
Edit Data CollectorThis functionality enables the user to edit the selected Data Collector.
Figure 7: Data Collector List - Edit
Delete Data CollectorThis functionally enables the user to delete the selected Data Collector.
Figure 9: Data Collector List - Delete A confirmation message is displayed:
Data Collector Search in Multi PassThis functionality enables the user to associate multiple Locations with a Data Collector. The purpose is to replace Multi Pass configuration setup from Setup Data Editor with a tabled interface and enforce unique Location to Device configuration.
Figure 11: Multi Pass Location
To add all Locations, click on Select All.
Print/Export Line Data CollectorThis functionality prints and exports the selected Line Data Collector configuration. The report results include Net User Id, Device Number, Line and Location Name of each Data Collector. The report prints to the default printer for the workstation.
Figure 13: Print Line Data Collector
A report is generated and the user is able to save the file or print it.
Print/Export Filtered Data CollectorsThis functionality prints and exports the Data Collectors filtered and displayed in the list. The report results include the Net User Id, Device Number, Line and Location Name of each Data Collector. The report prints to the default printer for the workstation.
Figure 15: Print Line Data Collector A report is generated and the user is able to save the file or print it.
Appendix A
Appendix BGlossary
it is a module that will set the permissions for users and external customers of Sanmina
the System Administration has full access - all plants, all reports, all users.
A component is a specific piece of data that appears on a label, for example: bar code, part numbers, graphic images, line or text. Hence, label components are broken down into several different types: text, graphic images, MDS database values, or a combination of text and database values.
In software development, a framework is a defined support structure in which another software project can be organized and developed. A framework may include support programs, code libraries, a scripting language, or other software to help develop and glue together the different components of a software project.
The rules used to define how SFDC collects data, provides analysis, controls processing and maintains unit histories
Universal login of Sanmina
the username is the siteminder username (or a partial string) Document Revision History
|