Difference between revisions of "42Q-MES0184-IIoT Configuration"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| | ||
| − | = <span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction">Introduction</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> = | + | = <span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction"><span class="mw-headline" id="Introduction">Introduction</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> = |
The concept of GGC stands for “Green Grass Computer”, the word: “Computer” also refers to any kind of device. This document will teach users how to configure, install, and deploy a GGC, as well as create and set up an Edge Device for the purpose of establishing a connection between the computer (device) and the 42Q portal to send data (payloads). | The concept of GGC stands for “Green Grass Computer”, the word: “Computer” also refers to any kind of device. This document will teach users how to configure, install, and deploy a GGC, as well as create and set up an Edge Device for the purpose of establishing a connection between the computer (device) and the 42Q portal to send data (payloads). | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| | ||
| − | = <span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites">Prerequisites</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> = | + | = <span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites"><span class="mw-headline" id="Prerequisites">Prerequisites</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> = |
*Only Linux is supported for the computer or device to install the Green Grass Core. The related shell scripts and test code only work on Linux systems (Windows is not currently supported). | *Only Linux is supported for the computer or device to install the Green Grass Core. The related shell scripts and test code only work on Linux systems (Windows is not currently supported). | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| | ||
| − | = <span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description">Functional Description</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> = | + | = <span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description"><span class="mw-headline" id="Functional_Description">Functional Description</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> = |
There are three different functional components: '''CloudPrinting''', '''MachineInterface''', and '''DataIngestion'''.<br/> To access the Edge Devices portlet, navigate to: '''Shop Floor Control > Configuration > IIoT Configuration > Edge Devices'''. | There are three different functional components: '''CloudPrinting''', '''MachineInterface''', and '''DataIngestion'''.<br/> To access the Edge Devices portlet, navigate to: '''Shop Floor Control > Configuration > IIoT Configuration > Edge Devices'''. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
| | ||
| − | = <span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software">Install 42Q Edge Software</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> = | + | = <span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software"><span class="mw-headline" id="Install_42Q_Edge_Software">Install 42Q Edge Software</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> = |
| − | == <span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting">CloudPrinting</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> == | + | == <span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting"><span class="mw-headline" id="CloudPrinting">CloudPrinting</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> == |
Please follow the steps below to create a 42Q Cloud Printing Edge Device in 42Q: | Please follow the steps below to create a 42Q Cloud Printing Edge Device in 42Q: | ||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
| | ||
| − | === <span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens">Testing Label Printing Function Using Label Engine Screens</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> === | + | === <span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens"><span class="mw-headline" id="Testing_Label_Printing_Function_Using_Label_Engine_Screens">Testing Label Printing Function Using Label Engine Screens</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> === |
#'''Navigate''' to: '''Administration > Label Engine Admin > Printer'''. | #'''Navigate''' to: '''Administration > Label Engine Admin > Printer'''. | ||
| Line 220: | Line 220: | ||
| | ||
| − | == <span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface">MachineInterface</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> == | + | == <span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface"><span class="mw-headline" id="MachineInterface">MachineInterface</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> == |
| − | This function is used for sending commands to machines from the cloud.<br/> Below there is an example | + | This function is used for sending commands to machines from the cloud.<br/> Below there is an example of stopping a machine when the server finds MSD material expired. |
| | ||
| Line 228: | Line 228: | ||
'''Figure 13: Server Stopping A Machine Due To Material Expired Diagram''' | '''Figure 13: Server Stopping A Machine Due To Material Expired Diagram''' | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EdgeDevice Diagram.png|900px]]<br/> |
The diagram above is divided into three steps: | The diagram above is divided into three steps: | ||
| Line 296: | Line 296: | ||
| | ||
| − | == <span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion">DataIngestion</span></span></span></span></span></span></span> == | + | == <span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion"><span class="mw-headline" id="DataIngestion">DataIngestion</span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span> == |
Please follow the steps below to create a 42Q Cloud Data Ingestion Edge Device in 42Q: | Please follow the steps below to create a 42Q Cloud Data Ingestion Edge Device in 42Q: | ||
Revision as of 21:42, 12 April 2023
42Q Home > IIoT > Device Self Service
Contents
Introduction
The concept of GGC stands for “Green Grass Computer”, the word: “Computer” also refers to any kind of device. This document will teach users how to configure, install, and deploy a GGC, as well as create and set up an Edge Device for the purpose of establishing a connection between the computer (device) and the 42Q portal to send data (payloads).
Prerequisites
- Only Linux is supported for the computer or device to install the Green Grass Core. The related shell scripts and test code only work on Linux systems (Windows is not currently supported).
- Python 3.8 or higher must be installed and configured to run the test code.
- Operating System and Software requirements:
- Linux kernel version 4.4 or later (Ubuntu 20.04 and CentOS 8.5).
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 8 or greater (included in the installation script).
- Python version 3.8 for functions that use the Python 3.8 runtime (included in the installation script).
- Network requirements:
A Region is an AWS region that hosts 42Q portal APIs. The Green Grass Core hardware needs to be able to access the following endpoints through specific ports:- https://www.amazontrust.com/repository/AmazonRootCA1.pem.
- https://d2s8p88vqu9w66.cloudfront.net/releases/greengrass-2.6.0.zip.
- greengrass-ats.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com. Ports: 8443, 443.
- .iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com. Ports: 8883, 8443, 443.
- .credentials.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com. Ports: 443
Functional Description
There are three different functional components: CloudPrinting, MachineInterface, and DataIngestion.
To access the Edge Devices portlet, navigate to: Shop Floor Control > Configuration > IIoT Configuration > Edge Devices.
Figure 1: Accessing Edge Devices
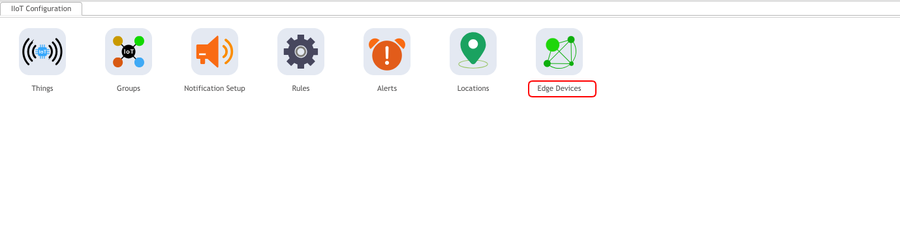
Figure 2: Edge Devices Functions
DSS Edge Devices Functions.png
- Users can query the list of all devices by Edge Device Name or Group Name.
- Users can create a new edge device.
- Users can view the details of the edge device.
- Users can download the software of the edge device.
- Users can upgrade this edge device with more features.
- Users can get all functional components through this button when no functional components are deployed on their local core device.
- Users can delete the edge device.
Install 42Q Edge Software
CloudPrinting
Please follow the steps below to create a 42Q Cloud Printing Edge Device in 42Q:
- Navigate to: Shop Floor Control > Configuration > IIoT Configuration > Edge Devices.
- Select CREATE EDGE DEVICE to create a new Green Grass Core.
Figure 3: CREATE EDGE DEVICE Button
DSS CREATE EDGE DEVICE Button.png
- Enter the Edge Device Name of the Green Grass Core. The name can be up to 128 characters. Valid characters are: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, colon (:), underscore (_), and hyphen (-).
- Select the Group Name as CloudPrintingGroup.
Note: After selecting the Group Name, the Group Version will automatically be selected.
Figure 4: Create Edge Device Form
DSS Create Edge Device Form.png
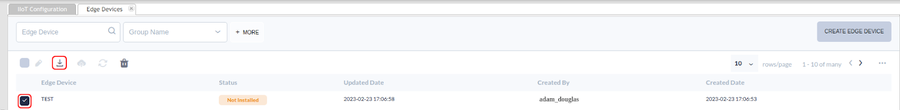
- Select the checkbox next to the desired Edge Device.
- Select the Download icon to download the Edge Device ZIP file.
Figure 5: Downloading The Files
- Right-click on the ZIP file.
- Select Extract Here to unzip the file.
- Open the Terminal.
- Enter the command: sudo su, and then press Enter.
- Enter the root user’s password, and then press Enter.
Note: If the word: root@ appears before the computer’s username as in the image below, it means that you are logged in as a root user.
Figure 6: User Logged In as a Root User
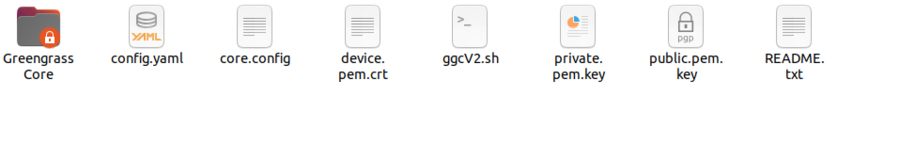
- Enter the next command: sh ggcV2.sh, and then press Enter.
Note: After the script is installed successfully, users can navigate to the local device’s path: /greengrass/v2 to check the installed folder; logs are contained in the path: /greengrass/v2/logs.
Figure 7: Edge Device Folder
Testing Label Printing Function Using Label Engine Screens
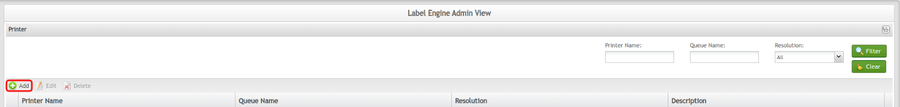
- Navigate to: Administration > Label Engine Admin > Printer.
- Select Add.
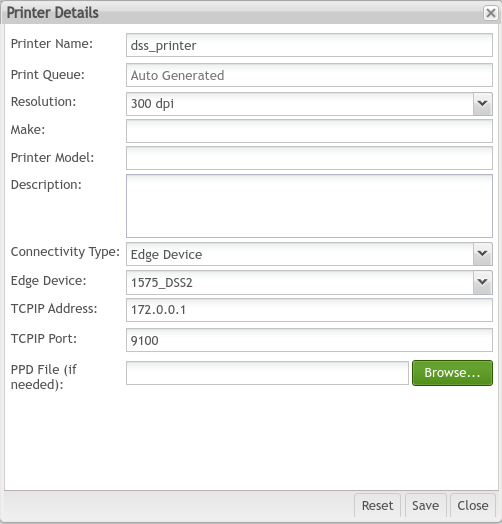
- Enter the Printer Name.
- Select theResolution from the drop-down list.
- Select the Connectivity Type as Edge Device.
Figure 9: Entering The Printer Details
Note: The TCP IP Address should be the address of the printer or start a TCP Server as a simulator by executing the next command in the Terminal: python3 tcpServer.py.
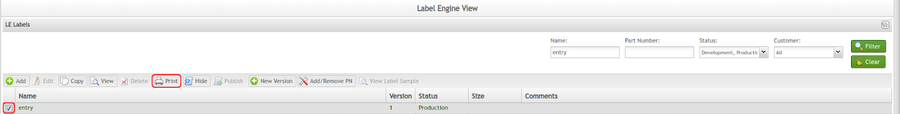
- Navigate to: Production > Label Engine Labels > LE Labels.
- Search for the label called “entry”, which will print whatever "Entry" value is passed.
- Select the checkbox next to the printer name.
- Select Print.
Figure 10: Print Button
- Select the Printer Name previously created.
- Enter a value in the Entry field.
- Select Test Print.
Figure 11: Entering Test Print Data
- Open the Terminal.
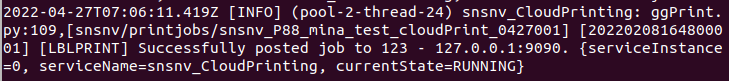
- Navigate to the local device’s path: /greengrass/v2/logs.
- Enter the next command: tail -f {envide}_CloudPrinting.log. After that, a message will be received to confirm the successful testing.
Figure 12: Successful Testing Message
MachineInterface
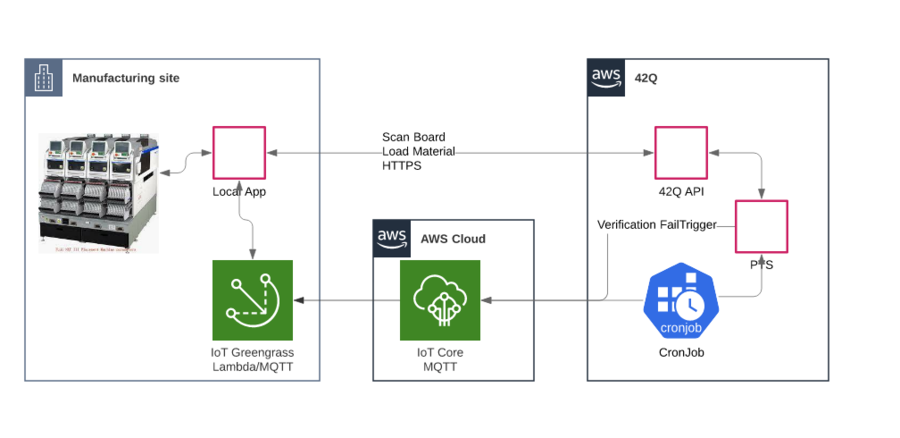
This function is used for sending commands to machines from the cloud.
Below there is an example of stopping a machine when the server finds MSD material expired.
Figure 13: Server Stopping A Machine Due To Material Expired Diagram
The diagram above is divided into three steps:
- Install an Edge Device on a server in the plant.
- The plant creates a new local application which can communicate with the Edge Device by TCP and also can send commands to machines.
- The Cloud application will send commands to the Edge Device, then the Edge Device will forward the message to the local application through TCP/IP.
Please follow the steps below to create a 42Q Cloud Machine Interface Edge Device in 42Q:
- Navigate to: Shop Floor Control > Configuration > IIoT Configuration > Edge Devices.
- Select CREATE EDGE DEVICE to create a new Green Grass Core.
- Enter the Edge Device Name of the Green Grass Core. The name can be up to 128 characters. Valid characters are: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, colon (:), underscore (_), and hyphen (-).
- Select the Group Name as MachineInterfaceGroup.
Note: After selecting the Group Name, the Group Version will automatically be selected.
- Select the checkbox next to the desired Edge Device.
- Select the Download icon to download the ZIP file.
- Right-click on the ZIP file.
- Select Extract Here to unzip the file.
- Open the Terminal.
- Enter the command: sudo su, and then press Enter.
- Enter the root user’s password, and then press Enter.
- Navigate to the extract folder by using the command: cd {folder path}.
- Enter the next command: sh ggcV2.sh, and then press Enter.
Note: After the script is installed successfully, users can navigate to the computer’s path: /greengrass/v2 to check the installed folder; logs are contained in the path: /greengrass/v2/logs.
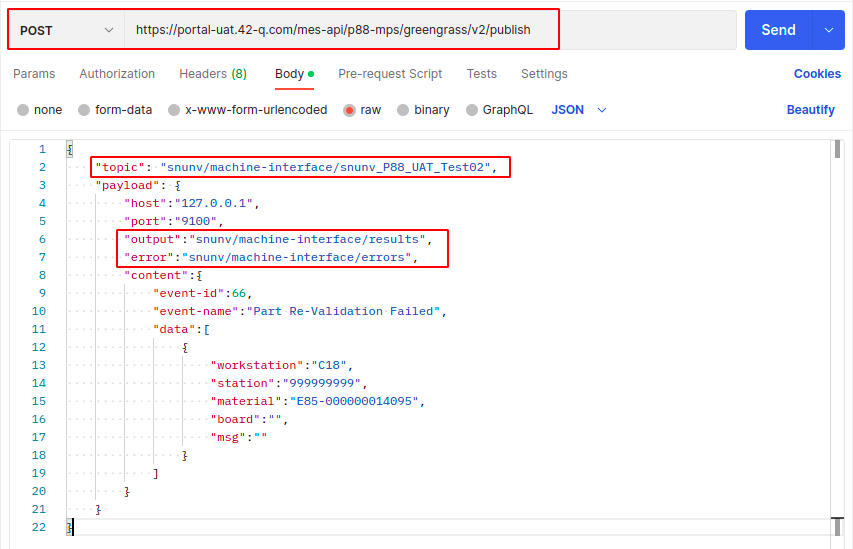
- Open Postman to test its functionality.
- Select POST as HTTP Method.
- Enter the URL.
- Enter the Topic.
- Enter the Output.
- Enter the Error.
Data nomenclature example:
URL: https://portal-uat.42-q.com/mes-api/[SiteName]/greengrass/v2/publish
Topic: [Envide]/machine-interface/[Envide]_[Edge device name]
Output: [Envide]/machine-interface/results
Error: [Envide]/machine-interface/errors
Figure 14: Sending The Payload Using Postman
- Open the Terminal.
- Navigate to the local device’s path: /greengrass/v2/log to view the logs.
Figure 15: Successful Payload Sending Logs
Note: If the message from the previous image is printed in your local log, the function has succeeded.
Adding the corresponding configuration for PTS allows PTS to send messages to Edge Device.
DataIngestion
Please follow the steps below to create a 42Q Cloud Data Ingestion Edge Device in 42Q:
- Navigate to: Shop Floor Control > Configuration > IIoT Configuration > Edge Devices.
- Select CREATE EDGE DEVICE to create a new Green Grass Core.
- Enter the Edge Device Name of the Green Grass Core. The name can be up to 128 characters. Valid characters are: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, colon (:), underscore (_), and hyphen (-).
- Select the Group Name as DataIngestionGroup.
Note: After selecting the Group Name, the Group Version will automatically be selected.
- Select the checkbox next to the desired Edge Device.
- Select the Download icon to download the ZIP file.
- Right-click on the ZIP file.
- Select Extract Here to unzip the file.
- Open the Terminal.
- Enter the command: sudo su, and then press Enter.
- Enter the root user’s password, and then press Enter.
- Enter the next command: sh ggcV2.sh, and then press Enter.
Note: After the script is installed successfully, users can navigate to the computer’s path: /greengrass/v2 to check the installed folder; logs are contained in the path: /greengrass/v2/logs.
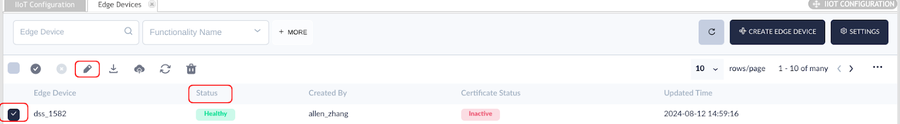
- When the status of this Edge Device is "Healthy", select the Edit button to enter the Edge Device information.
Figure 16: Edit Button
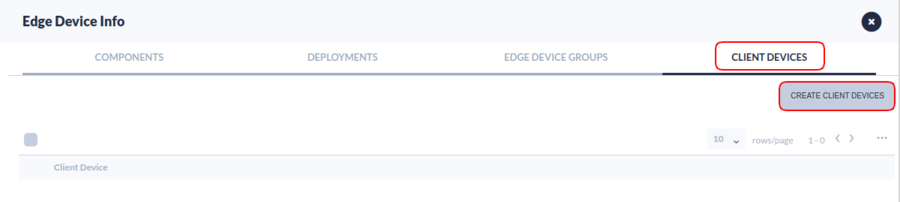
- Select the CLIENT DEVICES tab.
- Select CREATE CLIENT DEVICES.
Figure 17: CLIENT DEVICES TAB
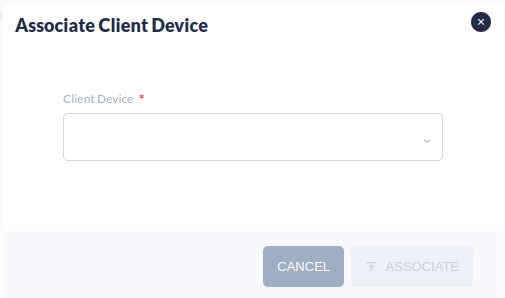
- Enter the name of the Client Device to be created.
Note: The name can be up to 128 characters. Valid characters: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, colon (:), underscore (_), and hyphen (-).
- Select ASSOCIATE.
Figure 18: Creating a Client Device
- Select the Download icon to download the Client Device ZIP file.
- Right-click on the ZIP file.
- Select Extract Here to unzip the file.
Figure 19: Client Device Folder
- Open the MqttTest.py file.
- Find the line that contains: ‘# Change This’.
- Modify the data information to be sent; users may see an example below (user’s will be different).
Figure 20: Data To Be Modified
- Open the Terminal.
- Enter the next command: python MqttTest.py, and then press Enter. The result should be similar to the image below:
Figure 21: Result Of Executing The MqttTest.py File
- Navigate to the local device’s path: /greengrass/v2/log to view the logs.
Figure 22: Successful MqttTest.py Running Logs
Note: If the message from the previous image is printed in your local log, the function has succeeded.
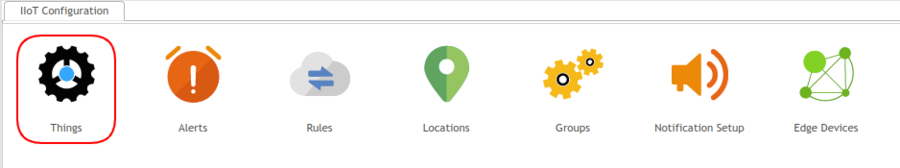
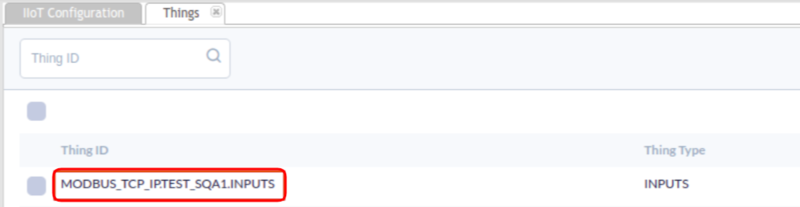
- Navigate to: Shop Floor Control > Configuration > IIoT Configuration > Things.
Figure 23: Things Portlet
- If the “Thing ID” is the same as the “id” configured in MqttTest.py file, it means that AWS Cloud has already stored the data uploaded.
- Navigate to: Reporting > IIoT Dashboard.
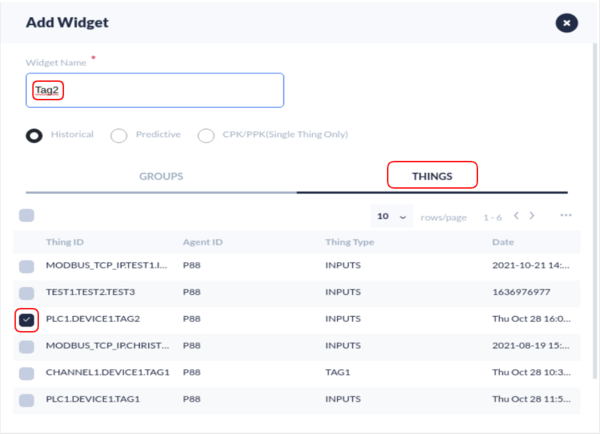
- Select the + icon to create a new widget.
- Enter the Widget Name.
- Select the THINGS tab.
- Select the "id" value previously configured in the MqttTest.py file.
- Select the SAVE button located at the end of the Add Widget Form.
Figure 26: Creating a Widget
- Select the show/hide icon to view the values of the widget created.
Figure 27: Show/Hide Icon
Note: Users can check the payload sent through either of the following:
- IIoT widget.