Difference between revisions of "SOP-42Q-MES0055 MESWeb Reports"
| Line 717: | Line 717: | ||
| | ||
| + | |||
=== Workstation Monitor Report === | === Workstation Monitor Report === | ||
| Line 756: | Line 757: | ||
14. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed | 14. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed | ||
| − | '''Figure | + | '''Figure 41: Workstation Monitor''' |
'''[[File:SOP-5-I-MES0055-C RA1 Workstation Monitor.jpg|RTENOTITLE]]''' | '''[[File:SOP-5-I-MES0055-C RA1 Workstation Monitor.jpg|RTENOTITLE]]''' | ||
Revision as of 21:29, 8 November 2018
42Q Home > Reporting > MESWeb Reports

This edition applies to MES15 Portal 1.0 Application and all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new revisions.
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Getting Started with MESWeb Reports
- 3 Accessing MESWeb Reports
- 4 Parameters
- 5 Steps
- 6 Results
- 7 Tools
- 8 Predefined Reports
- 8.1 Default Reports
- 8.1.1 Shop Order Report
- 8.1.2 Shop Order Summary Report
- 8.1.3 Top Defect Evolution Report
- 8.1.4 WIP Distribution Report
- 8.1.5 Yield & Defect Report
- 8.1.6 Yield Evolution Report
- 8.1.7 Yield Serials Report
- 8.1.8 Unit History Report
- 8.1.9 Part Order Summary Report
- 8.1.10 RTY Report
- 8.1.11 Workstation Monitor Report
- 8.1.12 WIP Serials Report
- 8.1 Default Reports
- 9 SOMS Reports
- 10 Document Revision History
Introduction
MESWeb is a powerful business intelligence application designed from the ground up to simplify reporting from manufacturing execution systems and to empower end users with a streamlined and full-featured web interface. The application includes an "ad hoc report" design tool that allows users to create basic, customized reports from heterogeneous data sources.
Decentralized custom reports, redundant data, lack of formal security controls, and convoluted development requirements are problems faced by all plants, and MESWeb has been designed to resolve these issues while maximizing usability and performance.
Business Benefits:
MESWeb provides access to technical information about MES through a real-time reporting database to avoid negatively-impacting production system performance by eliminating the need for an ODBC connection. In its standard configuration, some of the reports based on MES include the following, while new reports continue to be created:
- Work in Process (WIP Distribution)
- Yield, Defect, and Repair analysis
- Serial Number historical details (Unit History)
- Evolution Reports (including moving averages) – Top Defect Evolution and Yield Evolution
- Throughput information
These reports have the ability to filter and search data for common attributes such as Customer, Part Number, Process, Date and Time range, Shifts, Evolution Intervals, etc. These default reports provide a significant level of visibility to manufacturing processes.
Extensibility:
MESWeb is also the strategic platform for all MES reporting needs and it can be used with any system since the following databases are available:
- ERP
- Postgres
- MySQL
- SQL Server 2000-2005
- ODBC
Access Level
MESWeb has five distinct access levels:
- Administrator (System Administrator)
- Security Manager (Local Administrator)
- Report Manager
- Data Source Manager
- User (Execution Module only) Section Name
Administrator (System Administrator)
The System Administrator has full access to MESWeb Central and Execution – all plants, all reports, all customers. Basically, Administrator access includes the capabilities of all of the levels (Security Manager, Report Manager, and Data Source Manager). This access will be given to BSAs and global support personnel. An administrator can perform the following functions:
- Access the "Access Control" module
- Create, Edit, and Delete Locations
- Create, Edit, and Delete Data Sources
- Create, Edit, and Delete Data Source types
- Create new custom reports globally
- Copy, Edit, and Delete existing custom reports globally
- Publish custom reports globally
- Manage permissions for all MESWeb locations
Security Manager (Local Administrator)
The Security Manager has full access to the plant(s) where he/she has been designated as local Administrator for the MESWeb tool. The main responsibilities of this role are to organize permissions and manage customers. A Security Manager is able to:
- Visualize the Central MESWeb module in the MES Portal
- Access the "Access Control" module
- Grant permissions to him/herself and others from the Security Manager level to all lower levels
- Manage customers (add customers and map part numbers to them)
Report Manager
The Report Manager has access to "Reports" and "Report Groups" modules in the specific location(s) where he/she was designed as Report Manager. Inside those modules, a Report Manager is able to:
- Create custom reports and publish them only in his/her location
- Edit or Delete existing customer reports in his/her location
Note: Deleting is not possible if the report is published elsewhere
- Create Report Groups
- Add Reports to Report Groups
Data Source Manager
The Data Source Manager is responsible for creating and updating Data Sources and Data Source types.
A Data Source Manager is able to:
- Create, Edit, and Delete Data Sources
- Create, Edit, and Delete Data Source types
User (Execution Module only) Section Name
The User role is able to execute only those reports specifically granted access to him/her, and may not create new reports or modify existing reports. Administrators may restrict user access only to data belonging to specific customers and data sources.
Getting Started with MESWeb Reports
| MESWeb has been designed to be easy to use. The process of executing a MESWeb Report involves following only a few simple steps. Instructions for these steps may currently be found in two locations: (1) the MES Wiki (navigate to Reporting >
MESWeb) on the respective pages for each report; and (2) the MESWeb Report page (accessible via the MES Portal). Users who wish to read instructions for one or more specific reports are referred to the two aforementioned locations. Items that are important to the general use of MESWeb Reports are reviewed here. |
Accessing MESWeb Reports
| To access the MESWeb Reports page, users must have access to the 42Q Portal. Once logged in, users must navigate to Reporting MESWeb. The user is directed to the MESWeb Reports page. At this point the user ’
s web browser should be displaying content similar to that seen in Figure 1. |
Figure 1: Accessing MESWeb Reports
Users can access MESWeb Reports from this page by selecting Reports and navigating either to Default Reports or to SOMS. Figures 2 and 3 show a listing of the pages where users can generate the respective reports.
Figure 2: Default Reports
Figure 3: SOMS Reports
Figure 4 shows the appearance of a typical Report page in MESWeb. (Note that the instructions are provided in the window on the right-hand side of the page, whereas all user actions are performed in the window on the left-hand side of the page).
Figure 4: Report Page
Parameters
MESWeb has a collection of parameters highly configurable by the user to help filter the information.
Dropdown list
This manages a list where only one single option is selected (see Figure 5 for an example).
Figure 5: Dropdown List
Checkbox
A checkbox is used for true/false parameters (see Figure 6 for an example).
Figure 6: Checkbox
Radio Buttons
Radio buttons allow the user to select one (1) option from the list (see Figure 7). Every selectable option is mutually exclusive. This also can be used for showing different parameters.
Figure 7: Radio Button
Date
A date parameter is used to select a specific date. There is a variant that also allows the user to select a time.
Figure 8: Date
Date Range
Date range is a parameter that allows the user to select a range between two dates. There is a variant that also allows the user to select a time.
Figure 9: Date Range
Listbox
In a listbox, multiple options can be selected (i.e., users can select every option in the "Available" list). Users can filter options by using the radio buttons "Starts With", "Contains", and "Ends With". After the user selects the necessary option, he/she enters text into the text box and then must select the icon to refresh the list.
The (highlighted down-arrow) icon moves all of the options in the "Available" list to the "Selected" list.
The (down-arrow) icon moves only the selected option in the "Available" list to the "Selected" list.
The (up-arrow) icon moves only the selected option in the "Selected" list back into the "Available" list, thus removing it from the "Selected" list.
The (highlighted up-arrow) icon moves all of the options in the "Selected" list back to the "Available" list, thus removing all options from the "Selected" list.
Figure 10: Listbox
Multi-Line Text Box
The multi-line text box allows the user to add lines as necessary.
Figure 11: Multi-Line Text Box
Steps
Steps mainly work as filters that are used to execute reports. A step contains x parameters and it may or may not be the parent of another subsequent step. For example, after the user selects a Customer, the Part Numbers related to the selected Customer are shown.
Results
Grids
Once a report is executed, a grid with the results will appear on the right side.
Figure 12: Grids
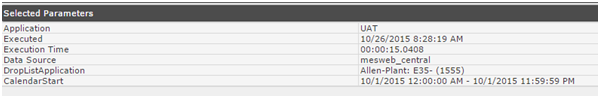
Selected Parameters
Selected parameters also appear down the side. These results contain other useful information such as the Application, the Execution Date, and the Execution Time.
Figure 13: Selected Parameters
Actions
There are three principal actions that can be done with the report s results: Print, Export, and Share.
This option allows the user to print the report.
Figure 14: Print Reports
After selecting Print, a dialog box appears. Select Print to display the report ’
s results.
Figure 15: Print Result
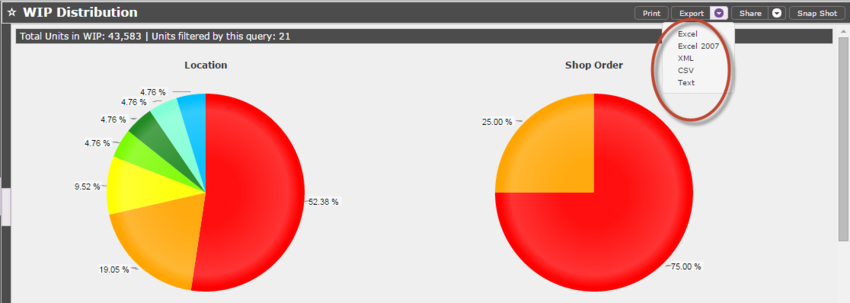
Export
The Export button downloads a file to the user s PC. The report can be saved in several formats (i.e., Excel, XML, CSV, and Text) depending upon the user s needs.
Figure 16: Export Report
This option is used to share the report ’
s results. The user can share the report via Email or as a Link.
Figure 17: Share Report Result
Drilldowns
Drilldowns occur when a link is selected by the user in order to drill down or further expand the data. To access Drilldown reports, select the parent link. This report will generate another report using a parameter passed by the selected link from the first report. This second report will use the default configuration (i.e., WEB format and pagination) to generate the data. WIP serials, a default report that shows the serial numbers and other information, has a Drilldown to Unit History. Drilldowns can be identified by their format; they are all underscored.
Figure 18: Drilldown Reports
Tools
Snap Shots
This tool allows the user to create Snap Shots of a report with the Selected Parameters displaying a certain time. These Snap Shots can be configured to run on a schedule.
Figure 19: Snapshot
Schedules
Schedules allow the user to create a task that will execute the report with the saved parameters from a Snap Shot.
Follow the steps below to create a Schedule:
1. Select the configuration icon in the top right corner of the page
2. Select Snap Shots within the list menu to open the Snap Shots window
Figure 20: Snap Shot Schedule
3. Select the plus-sign icon to the left of the Snap Shot to expand.
4. Select the plus-sign icon to the far right on the schedule bar to open the General Information form.
Figure 21: Snap Shot Additional Information
The General Information form appears where the user can enter specific information, such as Name, Time Zone, and Frequency, about the schedule (see Figure 22).
| The Frequency section allows the user to establish the timing settings for running a report. |
Figure 22: General Information
The Duration section allows the user to set a date range for execution. The user can also select how he/she would like the report to be delivered by choosing from the available options within the Delivery options section.
Figure 23: Duration and Delivery Options
In the example above, the report will be delivered via email in Excel format.
Figure 24: Sending
The fillable form shown in Figure 24 materializes when a user selects FTP in the "Via" drop-down list in the Delivery options section.
Figure 25: Sending via FTP Server
Once the FTP information has been entered and setup, the user can Save, Cancel, or Delete the scheduled report.
Most Viewed
MESWeb automatically saves the most viewed reports. These reports can be found within the Most Viewed group.
Figure 26: Most Viewed
Favorites
Every report has a star on the header that allows to user to save report on Favorites group.
Figure 27: Favorites
Predefined Reports
Predefined Reports are reports that cannot be changed in the Report Builder. These reports have more complex functions and are more complete. They can also be viewed graphically.
Sometimes, the user can see sub-reports in a Predefined Report. The most common Predefined Report is the Unit History Report, which allows the user to query data from multiple tables.
Default Reports
Shop Order Report
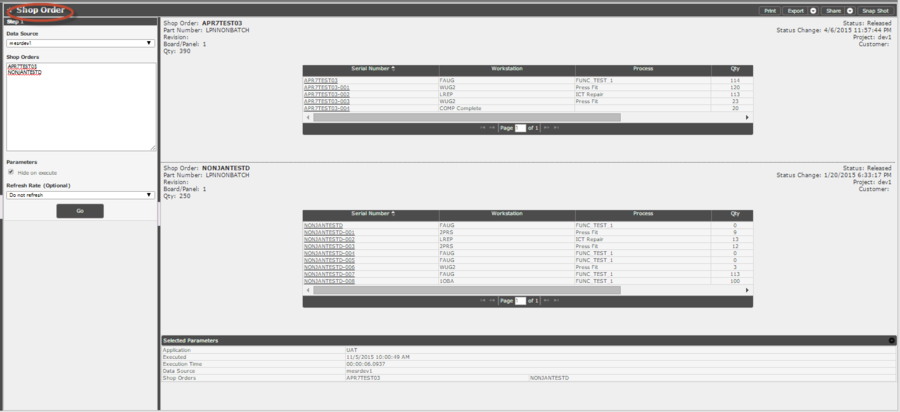
The Shop Order Report presents details for one or more shop orders along with all serials associated with them. It is important for users to track shop orders, and in order to do so, a user needs to be able to see the details of the units that comprise the shop order.
Follow the steps below to generate a Shop Order Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Enter up to 1000 Shop Order Numbers
3. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
4. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 28: Shop Order Report
Shop Order Summary Report
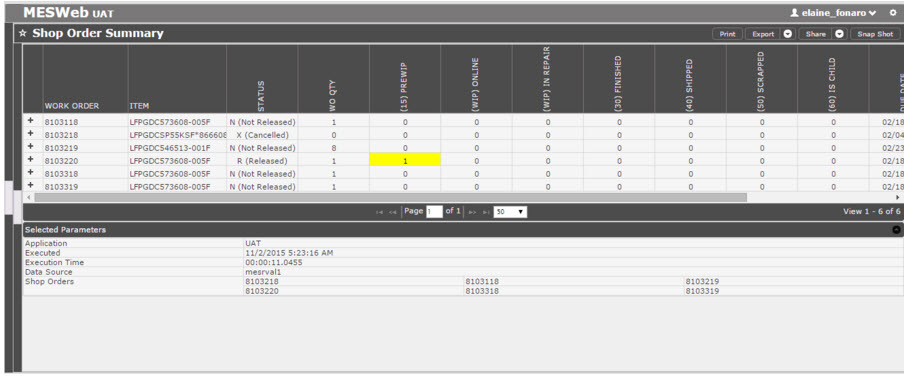
The Shop Order Summary Report displays information about the part numbers, the order status, and the quantity of units in each status of a shop order.
Follow the steps below to execute the Shop Order Summary Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Enter up to 100 Shop Orders (only one per line)
3. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
4. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 29: Shop Order Summary Report
Top Defect Evolution Report
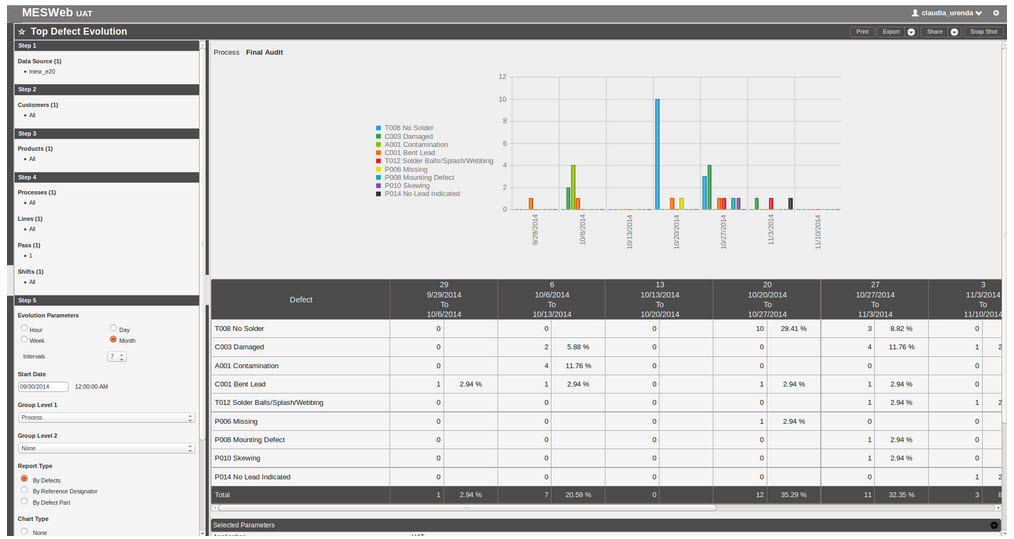
The Top Defect Evolution Report allows users to have a better view of defects registered in MESR for one or more products. Those defects are classified by defect name, which produces a sum (number of defects and percent defect from total) of defects found in a given range for the specific defect. This report also lists the defect total based on range of time.
Follow the steps below to generate a Top Defect Evolution Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Select one or more Customers
3. Select one or more Products
4. Select one or more Processes
5. Select one or more Lines
6. Select a Pass to view
7. Select one or more Shifts
8. Set the values for the Evolution Parameter
9. Select Start Date
10. Select which field to group by first
11. (Optional) Select which field to group by second
12. Select the type of report you want to run
13. Indicate if you would like to view graphs, and, if so, select the type
14. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
15. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 30: Top Defect Evolution Report
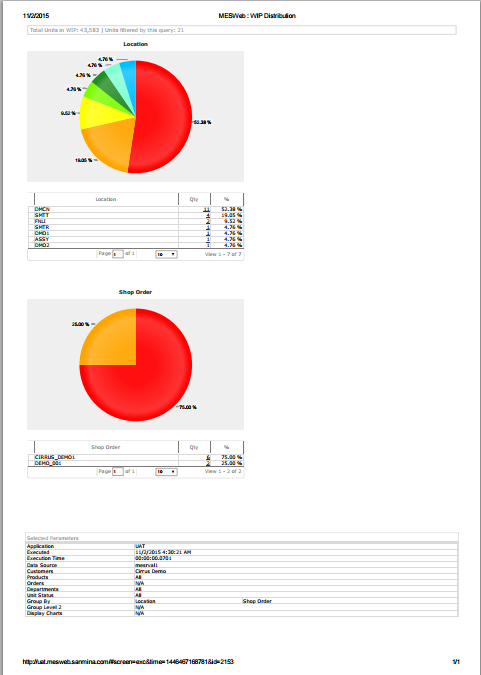
WIP Distribution Report
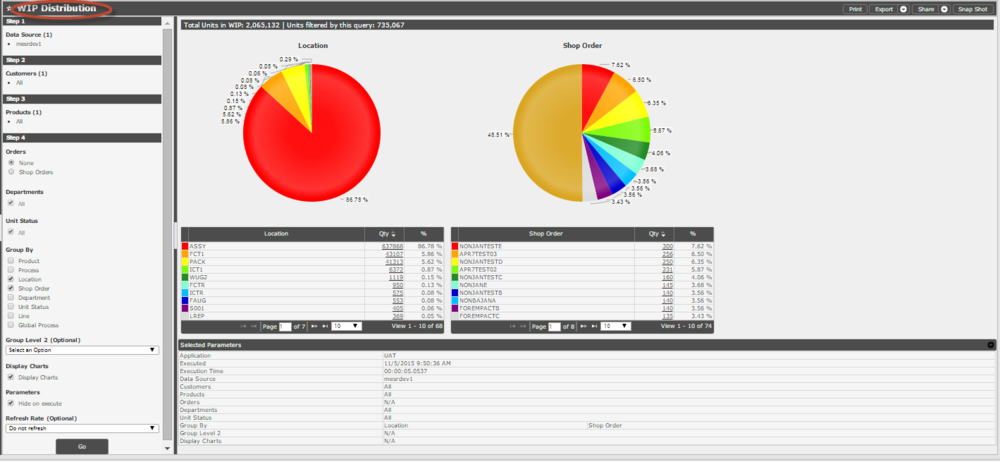
The WIP Distribution Report is designed to take the parameters specified by the user and return the number of units that are currently in WIP based on those parameters. The WIP Distribution Report can group results in several ways, depending on the user s preferences. The top level of the results offers the ability to drill down to the unit details. The WIP Distribution Report aims to give users the ability to get a snapshot of where their plant s workload is distributed.
Follow the steps below to generate a WIP Distribution Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Select one or more Customers
3. Select one or more Products
4. (Optional) null
5. Select one or more Departments
6. Select one or more Unit Statuses
7. (Optional) Select one or more Processes
8. Select one or more Workstations
9. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
10. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 31: WIP Distribution Report
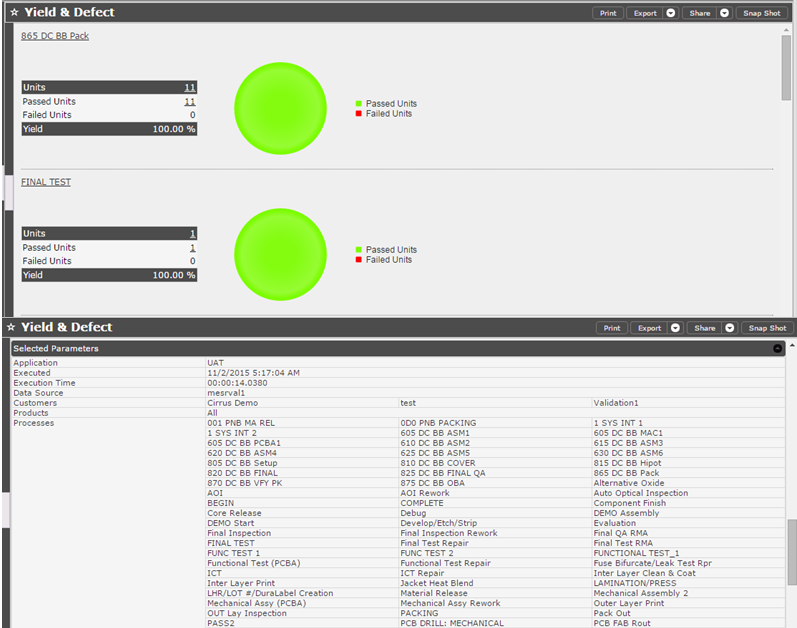
Yield & Defect Report
The purpose of the Yield & Defect Report is to give users a high-level overview of progress. It lists the total number of units with activity, pass/fail quantity, and the yield for each process that is selected (filtered by other parameters as well). From there users can see details about the most common defects for a given process as well as details about each unit.
Managers can use this information to pinpoint the areas on the floor that require their attention and discover why. To execute this report, the user must be in Execution Module, where he/she should select the Reports menu and navigate to Default Reports Yield & Defect Report.
Follow the steps below to generate a Yield & Defect Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Select one or more Customers
3. Select one or more Products
4. Select one or more Processes
5. Select one or more Lines
6. Select a Pass to view
7. Select one or more Shifts
8. Select one or more Workstations
9. Enter a Date Range or select one or more Orders
10. Select a field to group by
11. (Optional) Select a second field to group by
12. Choose whether to include moved units
13. Indicate if you would like to consider "No Fault Found" as passes
14. Indicate if you would like to view graphs
15. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
16. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 32: Yield & Defect Report
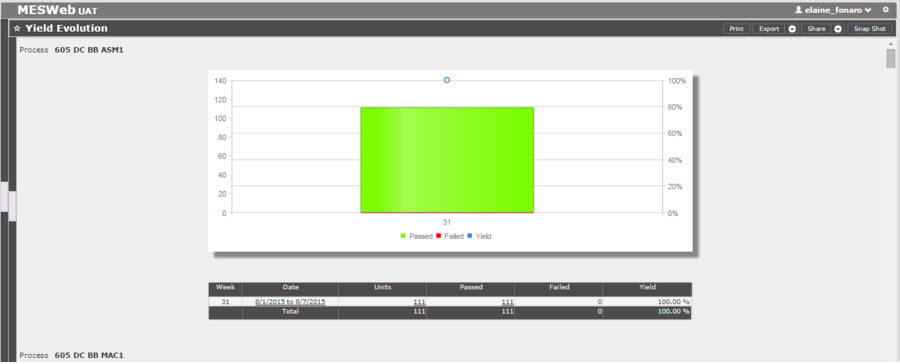
Yield Evolution Report
This report displays the percentage of success of the product for a determined period (Hour/Day/Week/Month). Users can view charts of this data and have tabular data presenting the hour/date/unit/passed/yield of a product. This data is presented via "All Products".
A Drilldown report, which offers more details about the product, is available for unit/passed/failed. To execute this report, the user must be in Execution Module, where he/she should select the Reports menu and navigate to Default Reports Yield Evolution Report.
Follow the steps below to generate a Yield Evolution Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Select one or more Customers
3. Select one or more Products
4. Select one or more Processes
5. Select one or more Lines
6. Select a pass to view
7. Select one or more Shifts
8. Set the values for the Evolution Parameter
9. Select Start Date
10. Select which field to group by first
11. (Optional) Select which field to group by second
12. Choose whether to include moved units
13. Indicate if you would like to display charts
14. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when report is executed
15. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 33: Yield Evolution Report
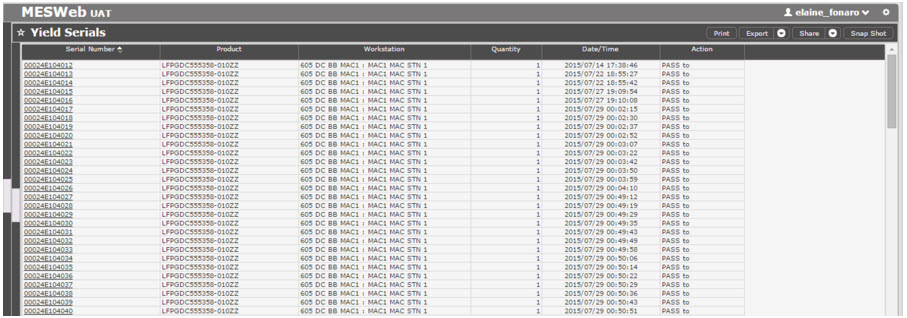
Yield Serials Report
The Yield Serials Report displays the following information: Serial Number, Product, Workstation where the action occurred, Serial Quantity, Date of Action, and the Action.
Follow the steps below to generate a Yield Serials Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Select one or more Customers
3. Select one or more Products
4. Select one or more Processes
5. (Optional) Select one or more Lines
6. Select a pass to view
7. (Optional) Select one or more Shifts
8. (Optional) Select one or more Global Processes
9. (Optional) Select one or more Workstations
10. (Optional) Filter data by a Date Range
11. (Optional) Select number of Shop Orders
12. Select one or more Actions
13. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
14. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 34: Yield Serials Report
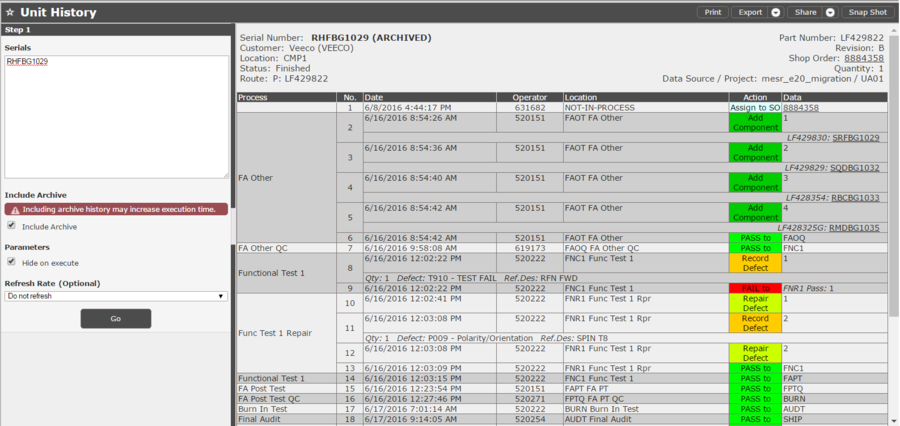
Unit History Report
The Unit History Report gives detailed information about a specific unit and all its activity throughout its lifecycle. This allows users to see information about a specific unit and its activity.
Follow the steps below to generate a Unit History Report:
1. Enter up to 1000 Serials
2. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
3. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 35: Unit History
Unit History Report now has the capability to query data from MES Archive integrated into the report. A new parameter was added to the report which allows the user to decide whether to query Archive data or only be notified when searched serials have already been archived.
New includes Archive Parameter.
Figure 36: Unit History
When the report is executed with the Include Archive parameter selected, it will query Archive data for all searched serials that have been archived. Archived serials will be labeled as such, and data will be presented in the same format as regular serials. Both archived and regular serials can be searched at the same time.
Report executed with Include Archive selected
Figure 37: Unit History
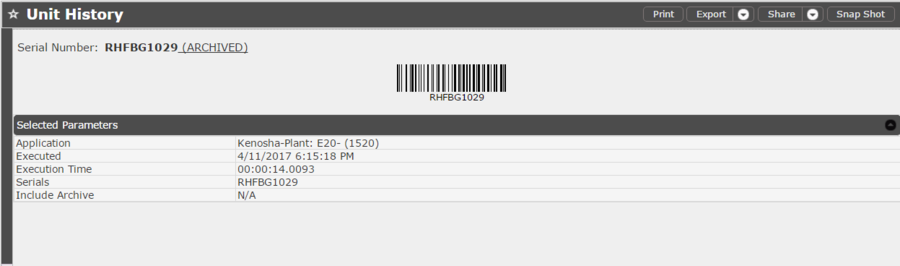
When the report is executed with the Include Archive parameter unselected, serials that have been archived will be labeled as such, and the user will be given the option to click the link in order to get the data from Archive. This is to prevent a longer execution time in case the user is unaware serials have been already archived.
Report executed with Include Archive unselected
Figure 38: Unit History
Part Order Summary Report
This report displays the following information about works orders: Part Number, Status, Quantity, and Serial Quantity. It also shows the due date, last activity and how many days has passed before the due date.
Follow the steps below to generate a Part Order Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Enter up to 500 Part Numbers (one per line)
3. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
4. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 39: Part Order Summary
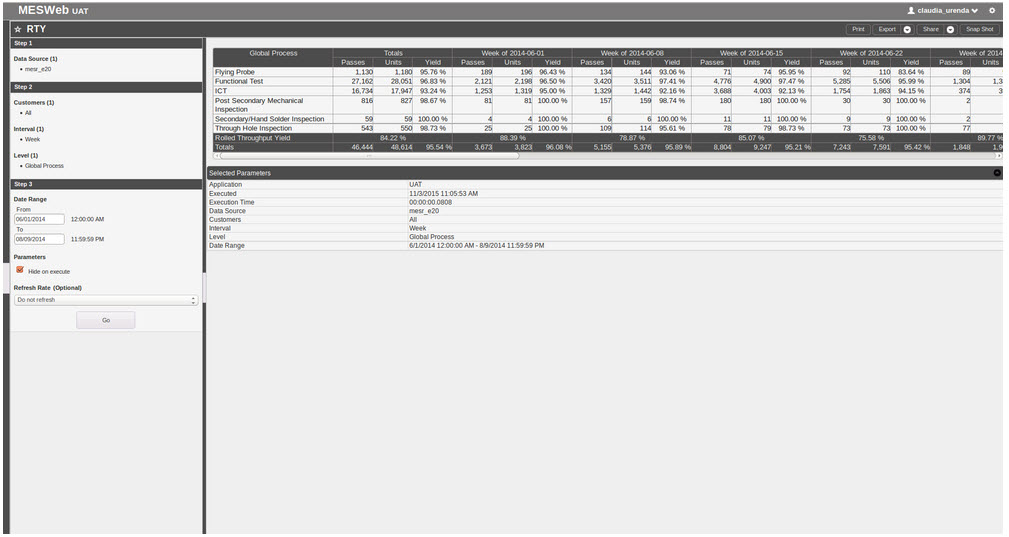
RTY Report
RTY shows how many activities were created by a Global Process. The report can display the results by month, week, or day.
Follow the steps below to generate an RTY Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Select one or more Customers
3. Select the Data Range (Start and End Dates)
4. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when report is executed
5. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 40: RTY Report
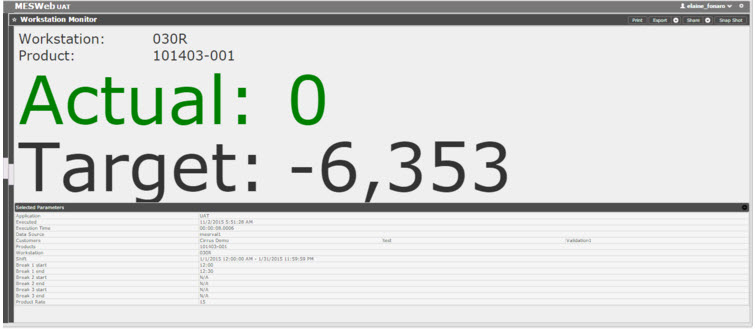
Workstation Monitor Report
The Workstation Monitor Report shows how many units have been processed on a particular station.
| Follow the steps below to generate a Workstation Monitor Report: |
1. Select a Data Source
2. Select a Customer
3. Select a Product
4. Select a Workstation
5. Select the Date and Time Range for the Shift
6. Enter the start time for the first break (format: HH:mm)
7. Enter the end time for the first break (HH:mm)
8. (Optional) Enter the start time for the second break (HH:mm)
9. (Optional) Enter the end time for the second break (HH:mm)
10. (Optional) Enter the start time for the third break (HH:mm)
11. (Optional) Enter the end time for the third break (HH:mm)
12. Enter UPH target.
13. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when report is executed
14. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 41: Workstation Monitor
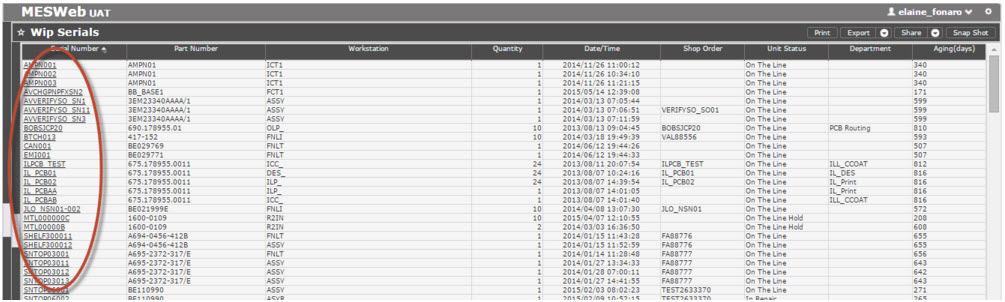
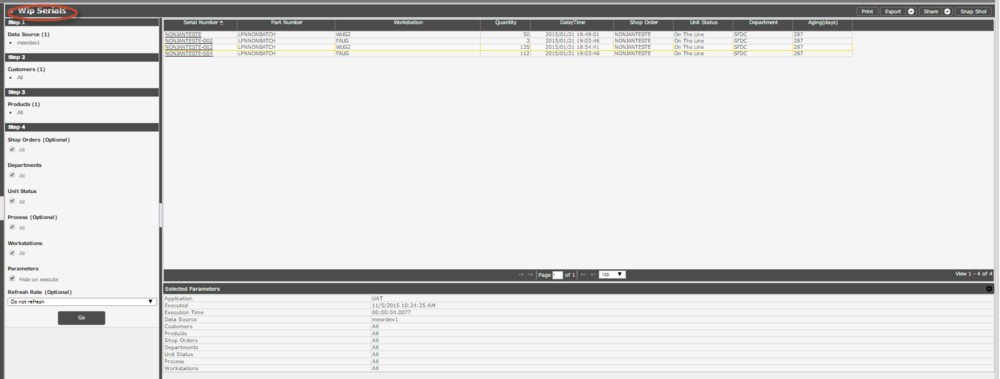
WIP Serials Report
The WIP (Work in Process) Serials Report displays all the serial numbers that are in production.
Follow the steps below to generate a WIP Serial Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. Select one or more Customers
3. Select one or more Products
4. Select the order that should be used to filter the results
5. Select one or more Departments
6. Select one or more Unit Status
7. Select one or more ways to group the information
8. (Optional) Select a field to group by
9. Indicate if you would like to display charts or not
10. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
11. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 39: WIP Serials
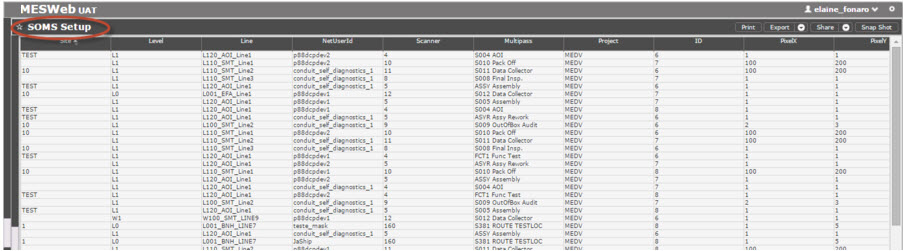
SOMS Reports
The SOMS Global Status Report is designed to start with a high-level overview of a plant ’
s current operating status. The user can see the current number of units that are in the WIP, the yield for the current and previous days, and the throughput for the current and previous days for each of the plant ’
s levels. Users also have the ability to drill down into a single level to see the same information broken out by line and process. The report is designed to give a quick snap shot of the health of a plant ’
s operation.
Follow the steps below to generate a SOMS Report:
1. Select a Data Source
2. (Optional) Enter the Mfg Line Name
3. (Optional) Enter the Scanner ID
4. (Optional) Enter the Multi-Pass Location Name
5. Select whether or not parameters should be hidden when the report is executed
6. (Optional) Select the interval to refresh the report as needed
Figure 40: SOMS Setup
Document Revision History
| Date | Author | Title | Version | Change Reference |
| 28/10/15 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | V1.0 | Initial Version |
| 12/01/16 | Claudia Urenda | Product Owner | V1.0 | General Review and especially for business rules. |
| 13/01/16 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | V1.0 | Small changes required and new images added. Format to WIKI format. |
| 15/01/16 | Kala Burson | Technical Writer | V1.0 | Grammatical edits. |
| 03/04/16 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | Updated Oracle occurrences to ERP |
| 28/04/16 | Dane Parker | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | Formatted to 42Q |
| 04/04/18 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | Applied new template for the format. |