Difference between revisions of "SOP-42Q-MES0007 Location Maintenance"
Dane parker (talk | contribs) m |
Dane parker (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== SFDC Configuration Setup == | == SFDC Configuration Setup == | ||
| − | + | As its name implies, the Shop Floor Data Collection (SFDC) system is responsible for the collection of data from the shop floor. The collected information is then stored in the Manufacturing Execution System (MES). Specifically, the real-time information collected by SFDC is utilized by Reporting and MES Web to create quality control reports. The SFDC system uses manual and automated barcode scanning to monitor and collect data for a product line or plant. Thus SFDC plays an important role in maintaining unit histories and directing product movement on the manufacturing floor. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
The system provides Access Control between the modules of the application, including the functionalities of each screen. The current version has an SFDC Configuration page which provides access to all sub modules pages and its functionalities (view, add, edit, delete, print and generate output file). | The system provides Access Control between the modules of the application, including the functionalities of each screen. The current version has an SFDC Configuration page which provides access to all sub modules pages and its functionalities (view, add, edit, delete, print and generate output file). | ||
Revision as of 16:17, 28 May 2014
Cirrus > Shop Floor Control > Configuration > Location Maintenance

This edition applies to MES15 Portal 1.0 Application and all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new revisions.
Contents
SFDC Configuration Setup
As its name implies, the Shop Floor Data Collection (SFDC) system is responsible for the collection of data from the shop floor. The collected information is then stored in the Manufacturing Execution System (MES). Specifically, the real-time information collected by SFDC is utilized by Reporting and MES Web to create quality control reports. The SFDC system uses manual and automated barcode scanning to monitor and collect data for a product line or plant. Thus SFDC plays an important role in maintaining unit histories and directing product movement on the manufacturing floor.
The system provides Access Control between the modules of the application, including the functionalities of each screen. The current version has an SFDC Configuration page which provides access to all sub modules pages and its functionalities (view, add, edit, delete, print and generate output file).
SFDC Configuration
1. To access SFDC Configuration, navigate to Shop Floor Control > Configuration > SFDC Configuration. The main SFDC Configuration and sub modules page is displayed:
Figure 1: MDS Portal – SFDC Configuration Sub modules
NOTE: A user only has access to the modules assigned to his/her profile.
Location Maintenance
The Location Maintenance record defines the location a process is performed in a product routing. All Location names begin with four characters, followed by a brief description of the process or function performed at the location.
As a general rule, locations are defined in the following order; Data Collector, Logical, then Physical Location. Once a location name has been defined, it is normally not changed. Be aware that modifying location names will impact historical reporting; therefore care should be taken when performing a modification.
- Data Collector Location: This location is sometimes referred to as Device Location and is named for the function performed and/or represents the physical placement of the device on the production floor. This is the location where data is collected. This is the only Location type listed in the Data Collector Table.
The Data Collector Location name follows the standard naming convention. The first character is always "S" for station. The next three digits are equal to the address scheme of the actual data collector or device number.
As a general rule, Data Collector Locations S001 through S999 are not used in routes, are not associated to a process name, and are always Status 20 On The Line.
When a data collector is initialized, the first 16 characters of the name will appear on the screen, therefore an accurate description of the process, or the devices physical location, is entered after the Snnn location name.
Figure 2: Data Collector Location Name Examples:
- Logical Location: Used as a holding area between scanning locations. Logical Locations provide for one or more physical locations to pass to multiple physical locations. It also allows one or more physical locations to receive from multiple physical locations. The Logical Location also helps provide accurate Work-In-Process reports.
As a general rule, Logical Locations are used for routing purposes only and reference a generic bucket (logical) location. All common Physical Locations (locations associated with the same process name) will receive from Logical locations in a Route by Process configuration, passing/failing to another Logical Location. Logical Locations will begin with four unique characters, followed by a space or underscore, then a brief description of the process name it is associated with.
Figure 3: Logical Location Name Examples:
- Physical Location: This location is specific to the physical placement of the data collector on the production floor. It shares the same process name as Logical Location but is unique to a specific device. A Physical Location sharing the process name with the Logical Location will receive units from it and pass to another Logical Location in a Route by Process configuration.
As a general rule, Physical Locations are not uses for routing purposes in Route by Process configurations. If Route by Process is not used, each scanning location must be defined in the route.
When defining Physical Locations, the first four characters are unique, followed by a space or underscore, then character positions six through nine should contain the first four characters of the Logical Location assigned the same process name. The remaining characters provide a brief description of the physical location of the device. This naming convention allows easy filtering in the location table, as the user only needs to filter the Logical Location name, and any Physical Locations with the same process name are returned.
Figure 4: Physical Location Examples:
- Multi-Pass Device Location: A secondary name for a Data Collector Location when it is used for multiple functions. Multi-Pass Devices are used when a product is going to be scanned at the same Data Collector more than once for multiple processes. Reference the section on Data Collector Maintenance for more information on configuring Multi-Pass Devices.
Early on, these types of locations were defined by an alphanumeric character other than the one used by the Data Collection Location, followed by the same three numeric characters, a space, then the remaining characters are the process name. For example, if the Data Collector Location is S001, the Multi Pass Location names assigned to that device number would be A001, B001, C001, and so forth. This is not intuitive to the operator as this name convention does not positively identify the process a unit passes or fails to. Therefore, the newer Physical Location naming convention, mentioned previously, has been developed.
List Locations
Based on the actual SFDC Configuration, the application displays a list with all Locations.
To list locations, select Location Maintenance from the SFDC Configuration page.
The Location List page is displayed:
Figure 5: Location List
In accordance with theunit status (see Appendix B), the line of the data collector list is displayed in the different colors as below:
Status = 20 On the Line with process name:green
Status = 28 On The Line Hold with process name: dark green
Status = 20 On The Line without process name: orange
Status = 28 On The Line Hold without process name: dark orange
Status = 25 In Repair: red
Status = 26 Outside Processing: green
Status = 27 In Repair Outside: dark red
Status = 29 In Repair Hold:dark rose
Status = 30 Finished: blue
Status = 50 Killed: gray
</font>Other Status: black
NOTE: Location Type = Repair only if it Unit Status is:
25 In Repair:red
27 In Repair Outside: dark red
or 29 In Repair Hold:dark rose
</font>
From this screen, the user is able to view a list of locations, as well as, add, edit or delete locations.
Add Location
This functionality enables the user to add a location to the Locations Table. All mandatory fields must be populated or an error messages is displayed.
Note: When a new Data Collector Location is created, a prompt is displayed to create a record in the Data Collector Table also.
1. To add locations, select Add from the Location Filter main screen.
Figure 6: Add Location
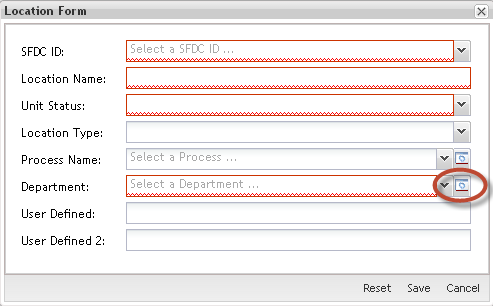
The Location Form is displayed:
2. Populate the mandatory fields;
SFDC ID: Each Location record must be attached to a SFDC ID.
Location Name: Each location must have a unique name. The name can be up to 20 characters: the first four characters must be unique and be followed by a space or underscore. The remaining 15 characters are used to describe the function or physical location.
Unit Status: Defines the status of a unit based on the status of the Location.
| On the Line |
Used at any Location that is a part of the normal manufacturing process or product flow. |
| On the Line Hold |
Same as On the Line with the added ability of allowing the unit to move from one SFDC PC to another within the same database. Also used to move from one route to another. When a unit has this status, the Serial record is removed from the SFDC PC and stored on the MDS server. It does not appear as part of the SFDC Work-In- Process report, but on the MDS Work-In-Process report. |
| In Repair | Used at any Location that is not considered part of the normal manufacturing process. In creating Routes, any unit with a defect is failed to a Location with an In Repair status. The unit continues to have this status unit all defects are repaired. A unit cannot be manually moved from a Data Collection Location with an In Repair status to a Location with On the Line status. Nor can a unit pass from this status to a Finished status. |
| In Repair Hold |
Combines the In Repair status with the secondary functions of the On Line Hold status. |
| Finished | Defines the unit as complete. Unless the product will be installed into an upper level assembly, the Route ends by passing a unit to a Location with a Finished status. When a unit passes to Finished Location, the Serial record is removed from the Current Serial records on the SFDC PC and is stored in History. If a unit is manually moved to a Finished Location from the SFDC PC, the Serial record is moved from Current to History at the next shift change. Neither SFDC nor MDS Work-In- Process reports include Finished status Locations. |
- For more information, see Appendix B. Unit Status Definitions.
Location Type: Kitting_Consolidation, Integration, Inspection, and Repair
Process Name: Defines the manufacturing process occurring at the Data Collection Location. It is used to group multiple Locations with the same function for SFDC and MDS reports. The Process Name is used to determine the number of times a unit passes through a Data Collection Location. It also supports SPC/SQC reports to group same function locations across multiple lines.
Note: To access Process Maintenance, click the Manage button.
Department:Defines the department that a location is assigned. Supports SPC/SQC reports across multiple Lines. All Locations must be assigned to a Department. The SOMS system uses department to define the line in which a location is associated.
Note: To access Department Maintenance, click the Manage button.
User Defined: Provides additional information about a Location. Also links Locations together for SPC/SQC or Reports applications. This is a 20-character text string. The SOMS system utilizes User Defined 1 as the Site Code.
Basic Maintenance - Departments
This functionality enables the user to manage Department names. Each location will be assigned to a department.
1. To access Department Maintenance, select Add Location or Location, then select Manage button for Departments field.
Figure 7: Add Location - Location Form
The maintenance page for Department displays:
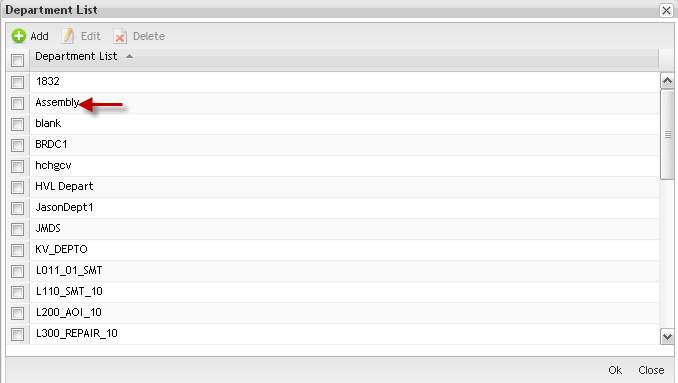
Figure 8: Department - Select a Department
Based on the actual SFDC Configuration, the application displays a list with all available departments. From this screen the user is able to list, add, edit and delete Departments.
Add Department
This functionality enables users to add or create Departments in the database.
To add a Department, select Add.
The Create Department screen is displayed:
Figure 09: Create Department
Enter the Department name;
Select OK to add/create the Department, or Close to cancel the operation.
The new Department is created and is displayed in the department list, making it available to select.
Edit Department
This functionality enable user to update an existing Department name.
Note: Once a department name has been defined, it is normally never changed. Be aware that modifying department names will impact historical reporting; therefore care should be taken when performing a modification.
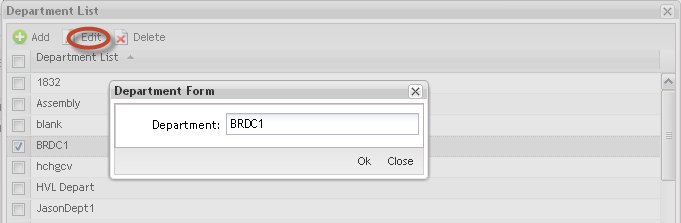
1. To edit the department name, select the Department to edit then select Edit.
The Edit Department page is displayed:
Figure 10: Edit Department
2. Perform the desired edit to the Department name.
3. Select Ok to confirm or Close to cancel the operation.
4. The Department name is updated and ready for use.
Delete Departments
This functionality enables user to delete the selected department.
Note: It is not possible to delete a department if activity has been recorded at a location while it was associated with it. It is also not possible to delete a department if it is associated with a location.
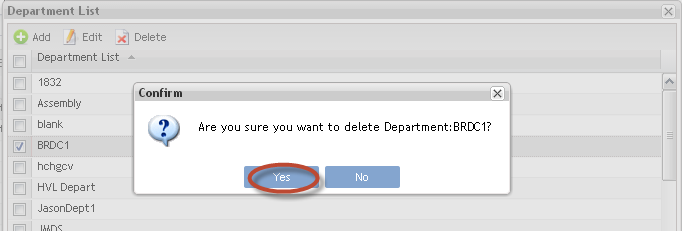
3. To delete a department name, select the Department, then select Delete.
A confirmation message is displayed:
Figure 11: Confirm
4. Select Yes to confirm or No to cancel the action.
5. The Department is deleted.
Process Maintenance
Process Maintenance can be found in multiple modules, for example; Attribute Def Maintenance, and Locations Maintenance modules. The functionality is to Add, Edit, Delete and Print Process Names in the database.
1. To access Process Maintenance table, select the Manage button for Process where applicable.
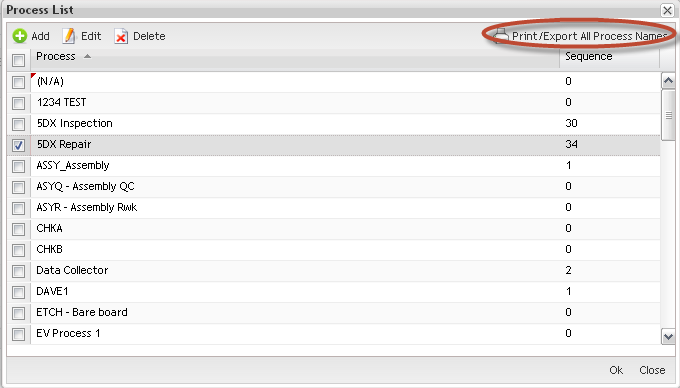
The Process Name Maintenance page is displayed:
Figure 12: Process Name Maintenance
Updated SOP-5-I-MDS0035-C RA1 MDS Location Maintenance 12.png
Based on the actual SFDC Configuration, the list of available Process Names is displayed.
From this screen, it is possible to List, Edit, Delete and Print/Export process names.
Add/Create Process Name
This functionality enables users to add or create Process Names in the database.
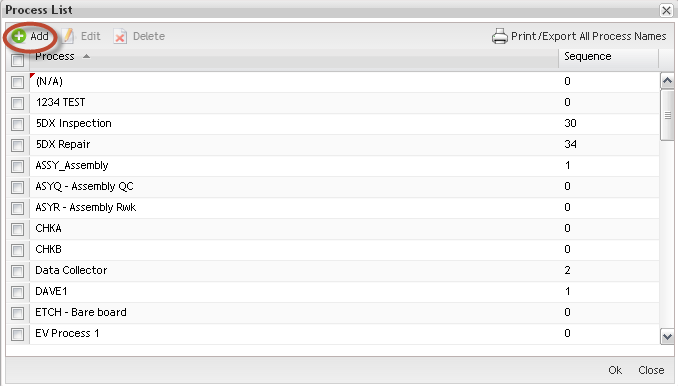
1. To add/create a Process Name, select Add.
Figure 13: Process Name - Add
The Create Process pop-up is displayed:
Figure 14: Process Name – Create Process Form
2. Enter the new Process Name;
As a general rule, Process Names should be clear and intuitive. This avoids the risk of confusion comprehending the process by users and operators.
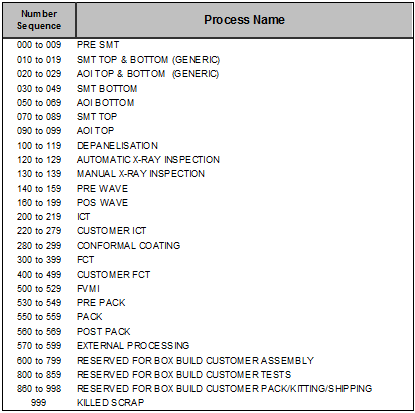
3. Enter Sequence Number. This is an optional field for use with the Sanmina Operational Management System (SOMS).
As a general rule, each plant will create a sequencing scheme that fits the business requirements. For example, one plant may only have sequence numbers for PCBA processes, while another plant for Box Build processes.
Sequencing scheme should follow production flow. For example. The process sequence for SMT_Inspection_1 would be lower than the process sequence for Functional_Test_1 as SMT processes occur prior to test processes. The Process Sequence conforms to SOMS requirements. The sequencing will aid in SOMS reporting as the processes will display in sequential order of the product flow. Process Sequencing also aids in grouping common Process Names.
Figure 15: Process Name Sequencing
4. Select Save to confirm.
Edit Process Name
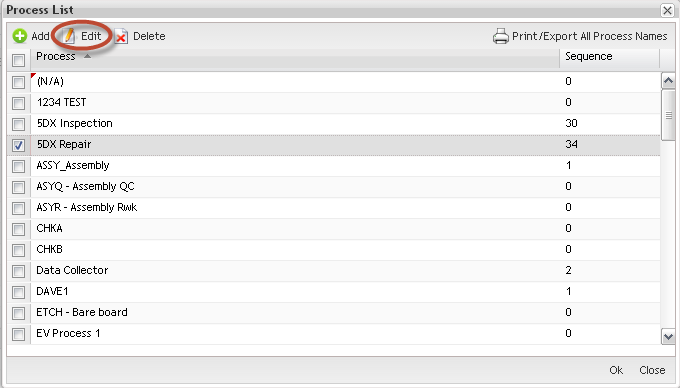
This functionality enables users to edit an existing Process Name in the database.
1. Select the Process Name to be edited and then select Edit.
Figure 16: Process Name - Edit
The Edit Process form is displayed:
Figure 17: Edit Process Name
2. Edit Process Name as desired.
3. Select Save to confirm or Cancel to exit.
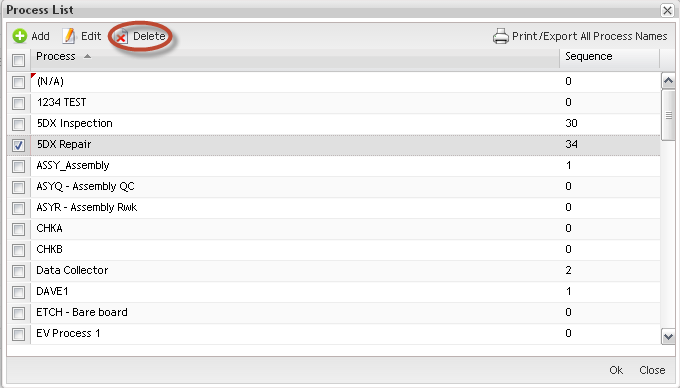
Delete Process Name
This functionality enables users to delete an existing Process Name, provided there has not been any activity records recorded against it.
1. Access Process Maintenance table by selecting the Manage button for Process where applicable.
2. Select the Process Name to be deleted then select Delete.
Figure 18: Process Name - Delete
A confirmation message is displayed.
Figure 19: Confirmation Message - Delete Process Name
3. Select Yes to confirm or No to cancel the action.
Print/Export Process Name
This functionality enables user to print and/or export Process Names.
To print the Process Names, select Print/Export All Process Names from the Process List.
Figure 20: Process Name - Print
A PDF report is generated and the user is able to save the file locally.
Figure 21: Print Export Report
1. Click on Print to print the report results.
Edit Location
This functionality enables user to modify or update an existing Location.
Note: Once a location name has been defined, it is normally never changed. Be aware that modifying location names will impact historical reporting; therefore care should be taken when performing a modification.
1. To edit a Location, select the Location to edit, and then select the Edit button in the list.
Figure 22: Location List - Edit
The Location Form page is displayed:
2. Make desired updates in the Location form and select Save to confirm the updates.
3. SelectCancel to cancel the update action.
4. The Location table is updated with the information provided in step 2.
Copy Location
This functionality enables user to Copy a selected Location.
1. To copy a Location, select the Location to copy, then select Copy.
Figure 23: Location List - Copy
The Copy Location pop-up is displayed:
2. Select the SFDC ID and fill the necessary fields.
3. Select Save to confirm, Cancel to exit, or Reset to clear all fields.
Delete Location
This functionality enables the user to delete an existing Location from the database
Note: It is not possible to delete a location if activity records have been recorded for the location.
1. To delete a Location, select the Location, then select Delete.
Figure 24: Location List - Delete
A confirmation message is displayed:
2. Select Yes to confirm or No to cancel the action.
3. The selected Location is deleted from the database.
Location – Where Used List
This functionality enables the user to generate a report displaying the Routes list.
1. To generate the report of where a location is used, click the Where Used List button.
Figure 25: Location List – Where Used
A PDF report is generated and the user is able to save the file locally:
Figure 26: Where Used Report
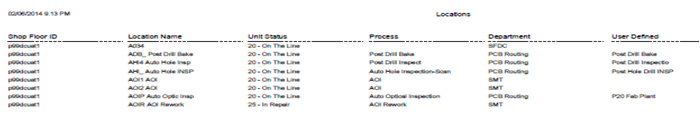
Print/Export Line Locations
This functionality enables the user to print and/or export the current Line Locations. The report results include the SFDC ID, Location Name, Unit Status, Process, Department, and User Defined of the selected Line. The report prints to the default printer for the workstation.
1. To print Line Locations, select Print/Export Line Location option in the Location Filter main screen.
Figure 27: Print Line Locations
The Choose SFDC ID popup is displayed:
2. Choose a SFDC ID.
A report is generated and the user is able to save it locally or print it.
Figure 28: Filtered Location Report
3. Select Print to print the report results.
Print/Export Filtered Locations
This functionality enables the user to print and/or export the filtered Locations. The report results include the SFDC I D, Location Name, Unit Status, Process, Department, and User Defined of filtered Locations. The report prints to the default printer for the workstation.
1. To print filtered locations, select Print/Export Filtered Location option in the Location Filter main screen.
Figure 29: Print Filtered Location
A report is generated and the user is able to save it locally and print it.
Figure 30: Filtered Report
Appendix A
Glossary
Access Control
it is a module that will set the permissions for users and external customers of Sanmina
administrator
the System Administration has full access - all plants, all reports, all users.
component
A component is a specific piece of data that appears on a label, for example: bar code, part numbers, graphic images, line or text. Hence, label components are broken down into several different types: text, graphic images, MDS database values, or a combination of text and database values.
framework
In software development, a framework is a defined support structure in which another software project can be organized and developed. A framework may include support programs, code libraries, a scripting language, or other software to help develop and glue together the different components of a software project.
SFDC Configuration
The rules used to define how SFDC collects data, provides analysis, controls processing and maintains unit histories
Site Minder
Universal login of Sanmina
username
the username is the siteminder username (or a partial string)
Appendix B
Unit Status Definitions
The following table provides a list of available unit status settings and their definitions (if available). See Locations Maintenance for more information.
| Released (10) | COPS status. Refers to Travelersbeing finalized. |
| Traveler Printed (15) | COPS status. Used when a Travelerfor a serial number is printed. Alsoused for Shop Order status when aserial number is assigned to a ShopOrder but not scanned at an SFDClocation yet. |
| On the Line (20) | Used at any location that is a part ofthe normal manufacturing process orproduct flow. |
| In Repair (25) | Used at any location that is notconsidered part of the normalmanufacturing process. In creatingroutes, any unit with a defect isfailed to a location with an In Repairstatus. Unless overridden by an Optionsetting in Setup Data Editor, the unitcontinues to have this status until alldefects are repaired. A unit cannotbe manually moved from a DataCollection Location with an InRepair status to a location with Onthe Line status. A unit cannot passfrom this status to a Finished status. |
| On the Line Hold (28) | Same as On the Line with the added ability to allow the unit to move from one SFDC PC to another within the same database. Also used to move from one route to another. When a unit has this status, the serial record is removed from the SFDC PC and stored on the plant server. It does not appear as part of the SFDC Work-In-Process report, but it does appear on the MDS WIP report. This location behavior can be overridden by an Option setting in Setup Data Editor. |
| In Repair Hold (29) | Combines the In Repair status with the secondary functions of the On Line Hold status. |
| Finished (30) | Defines the unit as complete. Unless the product will be installed into an upper level assembly, the route ends by passing a unit to a location with a Finished status. When a unit passes to Finished, the serial record is removed from the current serial records on the SFDC PC and is stored in history. If a unit is manually moved to a Finished location from the SFDC PC, the serial record is moved from current to history at the next shift change. Neither SFDC nor MDS WIP reports include Finished status locations. This is the only acceptable status when Kit stations are used in conjunction with COPS. |
| Container Open (34) |
|
| Container Close (35) |
|
| SFDC Internal (3) |
SFDC internal use status. |
| In Transit (37) |
|
| Shipped (40) | COPS status. |
| Temporary Ship Stati (45) | COPS status. |
| CRM Received (COPS) (46) | COPS status. |
| CRM Released (COPS) (47) | COPS status. |
| CRM RESERVED (COPS) (48) | COPS status. |
| CRM Finished (COPS) (49) | COPS status |
| Killed (50) | Originally a COPS status used to kill a serial number not to be shipped. Adapted for use in SFDC. When used, the serial number cannot be scanned by SFDC. |
| Pulled (55) |
|
| CRM Restart New (57) | COPS status. |
| CRM Restart Used (58) | COPS status. |
| Unit Component (60) | Defines a unit when it is a tracked component and has not been properly removed from the Top Level assembly. Requires a special Option line to be scanned again. |
| Unit Old ID (62) | Defines a serial number that was changed to another serial number. |
| Unit Skeleton (64) | Defines a unit serial number used for temporary copies of a real serial number. |
Document Revision History
| Date | Author | Title | Version | Change Reference |
| 08/15/13 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | This is the first revision of MDS User’s Guide |
| 02/07/13 | Ashley Martin | Technical Writer | v 1.0 | Grammar and images review |
| 02/07/13 | Elaine Fonaro | Technical Writer | V 1.0 | Formatting |